|
The Sun is the Source of Food Energy
Courtesy: McREL |
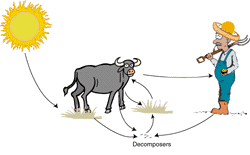
The sun is the major external source of the
energy, in the form of heat and light, needed to make the
Earth's processes work. The sun's light provides energy for
most life forms. Plants use sunlight, water, and minerals
they collect from the soil to form foodstuffs for themselves
and for animals. We eat plants and animals for food, ultimately
tracing the food energy back to sunlight. The sun's heat on
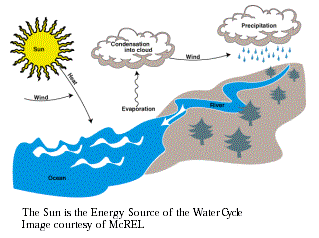
the Earth's surface and atmosphere provides the energy to
move the atmosphere and oceans, producing winds, ocean currents,
and the water cycle. The sun's heat and light maintain the
Earth's temperature. On a global scale, climate is determined
by the sun's energy affecting materials such as soil, rocks,
and water at and near the Earth's surface.
 |
The sun's heat and light energy are constantly
radiated from its surface in all directions. Early people
who attempted to relate observations of the sun with everyday
experiences interpreted the sun as a ball of fire or a hot
object. Now, scientists often describe the sun as an "invisible
fire," referring to its chemical and physical processes. How
does the sun produce heat and light in quantities sufficient
to be sent into space in all directions and still affect the
Earth 93,000,000 miles away?

Courtesy: NASA |
The sun, like all stars, contains mostly hydrogen.
It produces energy from nuclear reactions. In most common
chemical reactions, the outer parts of whole atoms, the electrons,
interact. Nuclear reactions are a type of chemical reaction
in which the nuclei of atoms interact, rather than the electron-bearing
surfaces of intact atoms. Interaction at the nuclear level
requires huge amounts of energy to initiate the reaction,
but at the same time releases unbelievable amounts of energy
during the reaction. In stars, the nuclear reactions are primarily
the fusion of hydrogen nuclei to form helium nuclei.
The temperature in the center of the sun is
an incredible 15,000,000 degrees (measured on the Kelvin scale).
At that temperature the hydrogen atoms are ripped apart, resulting
in a mixture of hydrogen nuclei and negatively-charged electrons
that are no longer part of an atom. A hydrogen nucleus is
a positively-charged particle called a proton. A helium nucleus
is a positively-charged group of four particles, two protons
and two neutrons. Where did those neutrons in the helium nucleus
come from? They are formed by the fusion of two protons. The
chemical equation for this fusion reaction looks like this:
proton + proton = deuteron + positron + neutrino
The protons are the hydrogen nuclei that make up 91% of the
atoms in the sun. The deuteron is a two-part object combining
a proton with a neutron. The neutron was formed from the mass
of one of the original protons, which was destroyed by the
reaction. The positive charge of the destroyed proton is carried
on the positron. The momentum of the escaping positron is
balanced by momentum of the uncharged neutrino.
It takes tremendous amounts of energy for protons
(hydrogen nuclei) to combine and change into neutrons. This
energy is supplied in the cores of stars by extreme heat and
high pressure.
Formation of a deuteron is the first step in
a star's creation of helium from hydrogen. In the next step,
a proton collides with a deuteron inside the sun to form a
helium-3 nucleus. This helium-3 nucleus is not normal helium,
since it has only two protons and one neutron. The chemical
equation for the second step in the sun's fusion reaction
is:
proton + deuteron = helium-3 nucleus
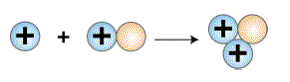
Formation of Helium-3. Courtesy:
McREL |
The third and final step is for two helium-3 nuclei to collide
and form a normal helium-4 nucleus and release two extra protons.
The chemical equation for this step is:
helium-3 nucleus + helium-3 nucleus = helium-4
nucleus + 2 protons
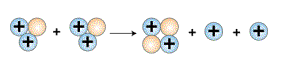
Formation of Helium-4. Courtesy:
McREL |
Of course, given the tremendous temperatures inside the sun,
the helium-4 nuclei will collide with protons and with each
other, creating still other types of chemical elements. These
fusion reactions and other similar processes in stars have
led to the formation of all the other natural chemical elements.

The Sun Provides Heat and Light
|
In the process of undergoing these nuclear fusion
reactions, the sun emits large amounts of heat and light.
This energy is a result of the positively-charged positrons
smashing into the loose electrons, and annihilating each other.
According to Einstein's famous equation, the total mass of
both positrons and electrons is destroyed, turning into energy.
This is the energy the Earth receives as heat and light.
Related Topics:
|
