|
|
![src="../../../images/spacer.gif"]() |
|
 |
 |
 Roping Rainbows can be a Blast! Join me in some fun stuff
while we play with sunlight! Roping Rainbows can be a Blast! Join me in some fun stuff
while we play with sunlight! |
 Why can I see myself in a mirror? Why can I see myself in a mirror? |
|
Reflection
of light occurs when light rays directed at an object
bounce off the object. Smooth, shiny surfaces, such as,
metals, glass, polished wood, and the surfaces of liquids
reflect light easily. |
 Why
does the sky change color? Why
does the sky change color? |
 |
 |
The
sky looks blue from Earth, but from space it looks black. |
 What
is the scattering of light? What
is the scattering of light? |
|
The
Earth's atmosphere is filled with lots of particles,
including atmospheric gas, water droplets, dust, pollen,
salt, and pollution. When light hits these particles,
it is scattered all directions. As the light is scattered,
different colors become visible. Scattering is responsible
for creating the blue of the daytime sky. |
| Here's
a fun activity that shows you how the sky changes color,
depending on where you are. |
 Why
are rainbows always bent? Why
are rainbows always bent? |
| Light
travels through the air in what appears to be a straight
line. But when a light ray passes from one substance to
another of different density, like from air to water,
the light ray changes speed and bends. This is called
refraction. As light travels from an area of high density
to an area of low density (for example from water to air),
it gains speed and bends. As light travels from an area
of low density to an area of high density (for example
from air to water), it slows down and bends towards the
normal. Refraction is responsible for many magnificent
atmospheric displays such as halos and rainbows. |
 Why aren't clouds square? Why aren't clouds square? |
| Diffraction
is the slight bending of light as it passes around the
edge of an object. In the atmosphere, diffracted light
is actually bent around atmospheric particles - most
commonly, the atmospheric particles are tiny water droplets
found in clouds. Diffracted light can produce fringes
of light, dark, or colored bands |
 What is a spectrum of colors? What is a spectrum of colors? |
Sunli ght
seen as white light is really a collection of many different
colors that the eye can detect. Different colors of light
are refracted at different angles when passing from air
into different matter (such as water or glass). A beam
of light sent through a prism is broken into many colors
called a spectrum. The colors have different wavelengths
and are refracted because the prism slows them down at
different rates. Violet and blue light have shorter wavelengths
and are bent the most, red and orange light have longer
wavelengths and are bent the least. The colors always
appear in the same order: red, orange, yellow, green,
blue, indigo, and violet. ght
seen as white light is really a collection of many different
colors that the eye can detect. Different colors of light
are refracted at different angles when passing from air
into different matter (such as water or glass). A beam
of light sent through a prism is broken into many colors
called a spectrum. The colors have different wavelengths
and are refracted because the prism slows them down at
different rates. Violet and blue light have shorter wavelengths
and are bent the most, red and orange light have longer
wavelengths and are bent the least. The colors always
appear in the same order: red, orange, yellow, green,
blue, indigo, and violet. |
 Why
do my legs look crooked when I dangle them in water? Why
do my legs look crooked when I dangle them in water? |
| Have
you ever dangled your legs in a pool or bathtub? Did they
appear to be crooked? You are seeing the effects of refraction.
Refraction is just a fancy way of describing light that
bends. It happens all the time. Have you ever put a straw
into a glass of water and noticed that it seemed to bend?
But when you pull the straw out, it is perfectly straight.
Hmmmmm. Light travels at different speeds, depending on
the substance in which it is traveling. Light moves more
slowly through water than air. As the light puts on the
brakes, it also changes direction a bit. |
 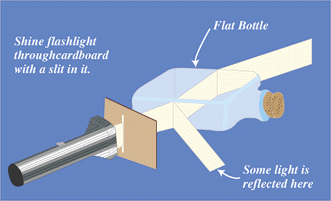 |
| When
sunlight enters the Earth's atmosphere, it encounters
the atoms and molecules of air. Blue light tends to bounce
off the atoms and molecules while the other colors of
sunlight travel straight to the surface of Earth. Since
blue light is scattered, it reaches our eyes from all
parts of the sky. Blue light coming in from all directions
gives the sky its blue appearance. The shade of blue depends
on the amount of water vapor and dust in the air. Water
vapor and dust scatter all colors of light, not just blue.
When dust particles in the air collect condensing water
vapor and become larger, the sky can turn from blue to
a hazy white. |
.gif) Astronauts
say that from space the sun appears Astronauts
say that from space the sun appears  white.
The sun would look white to us too if the blue light were
not scattered before reaching our eyes. The sun appears
yellow because yellow is what results when all of the
colors except blue are combined. When the sun is low on
the horizon (sunrise or sunset), sunlight enters the atmosphere
at a low angle and must pass through a great deal of the
atmosphere before being seen by an observer. When incoming
sunlight encounters very few particles in the atmosphere,
most of light reaches observers' eyes without being
scattered white or yellow sunsets. When incoming sunlight
encounters a heavy concentration of particles in the atmosphere
(like smoke, dust, salt, volcanic dust, and pollutants),
more violet and blue light is scattered resulting in a
red sunset. Red sunsets are often observed from a beach
because of the high concentration of salt particles suspended
in the air over the oceans. white.
The sun would look white to us too if the blue light were
not scattered before reaching our eyes. The sun appears
yellow because yellow is what results when all of the
colors except blue are combined. When the sun is low on
the horizon (sunrise or sunset), sunlight enters the atmosphere
at a low angle and must pass through a great deal of the
atmosphere before being seen by an observer. When incoming
sunlight encounters very few particles in the atmosphere,
most of light reaches observers' eyes without being
scattered white or yellow sunsets. When incoming sunlight
encounters a heavy concentration of particles in the atmosphere
(like smoke, dust, salt, volcanic dust, and pollutants),
more violet and blue light is scattered resulting in a
red sunset. Red sunsets are often observed from a beach
because of the high concentration of salt particles suspended
in the air over the oceans. |
 Can you match the image with the solar optic? (see
descriptions below) Can you match the image with the solar optic? (see
descriptions below)
 1. 1. |
Sun
Dog
Solar
Halo
Fogbow
Glory
Double
Rainbow
SolarPillar
Cloudbow
Corona
Answers |
 2. 2. |
 3. 3. |
 4. 4. |
 5. 5. |
 6. 6. |
 7. 7. |
 8. 8. |
|
Sun
Dog: A sundog is a brightly colored spot that appears
to the right or left of the sun. Sundogs form when the
sun is near the horizon and the sunlight is refracted
(bent) by hexagonal, plate-like ice crystals floating
horizontally in the air. Sundogs are brightest in winter
because ice crystals are more common, but can be seen
at any time. Sundogs are also known as mock suns or
parhelia.
Double
Rainbow: A double rainbow is two rainbows seen at the
same time. One is very bright, the second is dimmer
and on the outside of the main bow. The colors of the
second are in reverse order.
Solar
Pillar: At sunrise or sunset, a colorful pillar of light
can sometimes be seen directly above the sun. Solar
pillars are caused by sunlight reflecting off the flat
undersides of six-sided ice crystals shaped like flying
saucers. Only crystals floating directly above the sun
are at thecorrect angle to reflect sunlight to our eyes.
In foggy conditions, miniature pillars can sometimes
be seen above street lamps.
Solar
Halo: A solar halo is a ring around the sun. Haloes
are most often seen in cooler weather when conditions
are ideal for the formation of thin, milky sheets of
clouds that cover the sky but allow the sun to shine
through. Sunlight that is refracted (bent) by six-sided,
prism-like ice crystals floating randomly in the thin,
milky clouds create the halo effect. The same type of
halo can be seen around a full moon.
Cloudbow:
A cloudbow is a white rainbow. Cloudbows are similar
to rainbows but they appear white because the water
droplets are very tiny. Cloudbows are usually seen in
foggy conditions.
Corona:
Coronas occur when a thin cloud layer moves in front
of the sun or moon. The light that shines through the
cloud droplets curves (is diffracted) around the water
droplets. The diffracted light casts a light larger
than the original light source.
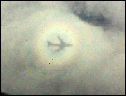
Glory:
A glory can often be seen surrounding an airplane's
shadow. It is a pale, circular rainbow caused by the
scattering and reflecting of sunlight from water droplets
in clouds below the plane. A glory is not a true rainbow
and is usually very small. Look for one the next time
you are on an airplane!
Fogbow:
Fogbow droplets are slightly larger than cloudbow droplets.
The droplets produce very weak colors. Fogbows are usually
seen in foggy conditions. |
 You
wanna get cooking? The sun can be a great source of heat
for making solar treats! You
wanna get cooking? The sun can be a great source of heat
for making solar treats! |

|
|
Want
to do some more cooking with the sun? Here is a link to
a student
activity on the Genesis Web site that shows you how
to build your own solar cooker, and you'll cook your own
hot dogs! If you don't have Adobe Acrobat Reader on your
machine, you can download it here:  |
|
