Sunwatchers
 Do
you like to travel? Come along and we'll
visit people and places from the past, stopping to have some
fun with me, the sun! Let's
go back in time. We know that for ages, people all over the
world have observed me, and there have been lots of ideas
about what I am. Do
you like to travel? Come along and we'll
visit people and places from the past, stopping to have some
fun with me, the sun! Let's
go back in time. We know that for ages, people all over the
world have observed me, and there have been lots of ideas
about what I am.
 What is a community of sunwatchers? What is a community of sunwatchers?
We
know that people have lived on the Earth for thousands of
years. They have lived in small and large communities, each
with its own ways of doing things. We know this by the things
these communities leave behind, sometimes hundreds of years
after the people who lived there are gone. These things are
often called artifacts. Artifacts
come in all sizes. Some are as small as a weaving tool and
can fit easily into your hand. Some artifacts weigh many tons.
Some communities have left enormous artifacts, like the Native
American Anasazi people who created a great city now in ruins.
As people have investigated these artifacts, we now understand
how advanced these people were. A community's artifacts
can show us their art, their tools for daily life, their homes,
and their belief systems. All of these things make up what
we call a culture. A culture represents a group of people
who live in a particular period, who form a community, who
share and practice traditional activities, who share a belief
system, and who may share the same ancestors.
 Hundreds--even
thousands--of years from now, what will the artifacts that
YOU leave behind tell future generations about your culture? Hundreds--even
thousands--of years from now, what will the artifacts that
YOU leave behind tell future generations about your culture?
 What does culture have to do with science? What does culture have to do with science?
People
who study artifacts over long periods of time are known as archaeologists. Their studies
show us that the sun has been a powerful and mysterious force
in people's lives throughout history--going back thousands
of years! Communities of sun watchers all over the world have
used the sun as a scientific tool to determine when to plant
their crops, tell time, explain natural marvels, and understand
the world. Like culture, science forms its understanding of
the sun based on the known facts at that time. We have a lot
of information on the sun today that has been enhanced over
time by using the contributions of people around the world
from today and from the past.
 Is archaeology the only way to study cultures? Is archaeology the only way to study cultures?
Archaeoastronomy is another way to study cultures and their histories. Archaeoastronomers
study archaeology, anthropology, and mythology as they are
linked to astronomy. They believe that by blending both material
things and oral stories, they can get a bigger picture of
a community of people, and how they interacted with their
world. Before archaeology, and even before world cultures
recorded their history in writing, oral story telling was
the way people preserved history and passed down knowledge.
Anxious not to lose their rich heritage, most cultures assigned
one person to serve as a keeper of the stories. This was a
highly regarded social position that brought great responsibility.
For these storytellers, truth in history was the goal.
Around
7000 years ago--long before the pyramids were constructed
in Egypt--people built structures aligned to the sun and stars
that served much like a sundial. They are the oldest dated
artifacts left to us by a culture. These stones are aligned
with the sun and the moon, making us believe they were built
in order to track time and predict the changes of the seasons.
 Where
is the oldest known sundial? It's in Africa, in southern
Egypt, at Nabta, and dates back over 6,000 years! The Standing
Stones at Nabta was built by a community of people who lived
off the land and its water. When the people of Nabta moved
on, they left the oldest known megalith on Earth, that covers
approximately one square mile. Where
is the oldest known sundial? It's in Africa, in southern
Egypt, at Nabta, and dates back over 6,000 years! The Standing
Stones at Nabta was built by a community of people who lived
off the land and its water. When the people of Nabta moved
on, they left the oldest known megalith on Earth, that covers
approximately one square mile.
Nabta
consists of a stone circle. The circle is created by a series
of flat and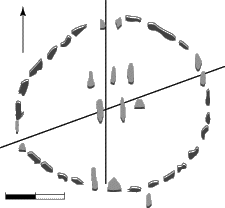 tomb-like stone structures with five lines of standing and
leaning megaliths extending outward and beyond the main circle.
Some of the stones used at this site are over nine feet tall
and were transported at least two miles. The people who created
this megalith used and positioned the stones in ways to help
them mark the passing of seasons and to determine rainfall
for the planting of crops. The
site also contains all kinds of cultural artifacts, including
small, fire-blackened stones from ancient hearths built along
the ancient lakeshore as well as manos (hand-held stones for grinding grain), metates (the stone on which the grains were ground), pieces of decorated
pottery jars, grains of sorghum, carved, decorated ostrich
eggshells, numerous bones of cattle, a sculptured rock resembling
a cow. What do these artifacts, including the placement of
the standing stones, tell you about the people of Nabta and
the things or practices that they valued as a culture? The
Standing Stones at Nabta served very much like another stone
structure built later in England. We call these structures megaliths. tomb-like stone structures with five lines of standing and
leaning megaliths extending outward and beyond the main circle.
Some of the stones used at this site are over nine feet tall
and were transported at least two miles. The people who created
this megalith used and positioned the stones in ways to help
them mark the passing of seasons and to determine rainfall
for the planting of crops. The
site also contains all kinds of cultural artifacts, including
small, fire-blackened stones from ancient hearths built along
the ancient lakeshore as well as manos (hand-held stones for grinding grain), metates (the stone on which the grains were ground), pieces of decorated
pottery jars, grains of sorghum, carved, decorated ostrich
eggshells, numerous bones of cattle, a sculptured rock resembling
a cow. What do these artifacts, including the placement of
the standing stones, tell you about the people of Nabta and
the things or practices that they valued as a culture? The
Standing Stones at Nabta served very much like another stone
structure built later in England. We call these structures megaliths.
 What are megaliths? What are megaliths?
Mystery
surrounds the giant stone structures (or megaliths) that were
built by ancient cultures. The most famous of these megaliths
is Stonehenge, located on the Salisbury plain in England.
However, there are many megaliths around the world from Europe
to Africa to America. Three types of megaliths are: 1) solitary
menhirs (large, single, upright stones), 2) circular menhirs,
(stones that form a circle), and 3) temples (generally built
for worship).
 How
was Stonehenge (the name means hanging stones) built with
stones that were not found in the area at that time? The Heel
Stone (the stone that some people believe defines the direction
of sunrise at the time of solstice)
weighs in at 35 tons! (Learn more about solstices and the
seasons here.) According
to local legend, the stones were moved magically by Merlin,
the magician from King Arthur's court. No one knows for
certain that Stonehenge was built to mark time. We do know
that it took a long time to build and is made up of a series
of earth, timber, and stone structures that were changed and
remodeled over a period of more than 2000 years. There are
91 stones that make up Stonehenge. From the air, you can see
that most of the stones are located within a large ditch.
Within this outermost circle are 56 round patches of white
chalk that modern astronomers can use to predict a solar eclipse.
At the center point you can see the sunrise above the heel
stone that is located outside of the circular ditch. How
was Stonehenge (the name means hanging stones) built with
stones that were not found in the area at that time? The Heel
Stone (the stone that some people believe defines the direction
of sunrise at the time of solstice)
weighs in at 35 tons! (Learn more about solstices and the
seasons here.) According
to local legend, the stones were moved magically by Merlin,
the magician from King Arthur's court. No one knows for
certain that Stonehenge was built to mark time. We do know
that it took a long time to build and is made up of a series
of earth, timber, and stone structures that were changed and
remodeled over a period of more than 2000 years. There are
91 stones that make up Stonehenge. From the air, you can see
that most of the stones are located within a large ditch.
Within this outermost circle are 56 round patches of white
chalk that modern astronomers can use to predict a solar eclipse.
At the center point you can see the sunrise above the heel
stone that is located outside of the circular ditch.
 Did
you know that over 3000 years ago, people in the United States
began building a large timepiece? Did
you know that over 3000 years ago, people in the United States
began building a large timepiece?
The
Big Horn Medicine Wheel, located near Sheridan, Wyoming, is
one of  several
stone circles throughout the continental United States and
Canada. It is believed to have been originally constructed
by Native Americans in 1500 B.C. with construction ongoing
through 500 A.D. Although the information about the medicine
wheel is recent, there is evidence that people used it to
predict seasonal changes. When you stand in the middle of
the wheel, called the hub, an alignment scheme becomes evident.
The spokes on the wheel correspond to various celestial phenomena
like the summer solstice and the rising of stars-Rigel,
Aldebaran, and Sirius. These events occur during times when
this area could have hosted nomadic people. It is believed
that the people used this eel to determine when it was time
to move to another camp site. several
stone circles throughout the continental United States and
Canada. It is believed to have been originally constructed
by Native Americans in 1500 B.C. with construction ongoing
through 500 A.D. Although the information about the medicine
wheel is recent, there is evidence that people used it to
predict seasonal changes. When you stand in the middle of
the wheel, called the hub, an alignment scheme becomes evident.
The spokes on the wheel correspond to various celestial phenomena
like the summer solstice and the rising of stars-Rigel,
Aldebaran, and Sirius. These events occur during times when
this area could have hosted nomadic people. It is believed
that the people used this eel to determine when it was time
to move to another camp site.
 We've
seen menhirs. How do sun temples fit in? We've
seen menhirs. How do sun temples fit in?
 Sun
temples are found all over the world. These temples (many
of which are now in ruins) show us that ancient people observed
and revered the sun. You can find sun temples in many countries,
including India, Pakistan, Egypt, Central America, and Mexico. Sun
temples are found all over the world. These temples (many
of which are now in ruins) show us that ancient people observed
and revered the sun. You can find sun temples in many countries,
including India, Pakistan, Egypt, Central America, and Mexico.
 The
sun is believed to be the source of life for the people of
India. Over a thousand years ago, temples and shrines were
built in the Tamil Nadu (known as the "Land of the Temples"
region. On days close to the equinox the sun shines at dawn
or sunset on the main deity--generally the benevolent sun
god, Surya--of that temple. One of the most well-known temples
of India is Konark in Orissa on the eastern seashore of the
country. The present temple at Konark, also known as the Black
Pagoda, was built over 700 years ago. Konark resembles a great
chariot with seven horses and 24 wheels with eight spokes
in each wheel. It is believed that the seven horses represent
the days of the week. Different sources report that the wheels
represent either the hours of the day or each month in the
Hindu calendar with the spokes being one of the part of the
Hindu day. The
sun is believed to be the source of life for the people of
India. Over a thousand years ago, temples and shrines were
built in the Tamil Nadu (known as the "Land of the Temples"
region. On days close to the equinox the sun shines at dawn
or sunset on the main deity--generally the benevolent sun
god, Surya--of that temple. One of the most well-known temples
of India is Konark in Orissa on the eastern seashore of the
country. The present temple at Konark, also known as the Black
Pagoda, was built over 700 years ago. Konark resembles a great
chariot with seven horses and 24 wheels with eight spokes
in each wheel. It is believed that the seven horses represent
the days of the week. Different sources report that the wheels
represent either the hours of the day or each month in the
Hindu calendar with the spokes being one of the part of the
Hindu day.
 Other
than megaliths, are there any other ways that we know ancient
cultures marked time? Other
than megaliths, are there any other ways that we know ancient
cultures marked time?
 Around
700 years ago, in North America, three different communities
of people built observatories to mark time with the sun. One
of these is the Pyramid at Chichen Itza. In order to predict
events on the solar calendar, like the equinoxes, solstices,
and eclipses, the Mayans built observatories. One such observatory,
called El Castillo, was built in an area called Chichen Itza.
It is believed to be a temple, or a place of sun worship.
This pyramid has a square base with nine terraces built upward.
Each terrace contains a set of 18 steps, which corresponds
to the 18 months of the Mayan Calendar. There are 91 stairs
on each side of the pyramid, totaling 364 steps. By adding
the platform to this figure, the total is 365 representing
the days in a solar year. Around
700 years ago, in North America, three different communities
of people built observatories to mark time with the sun. One
of these is the Pyramid at Chichen Itza. In order to predict
events on the solar calendar, like the equinoxes, solstices,
and eclipses, the Mayans built observatories. One such observatory,
called El Castillo, was built in an area called Chichen Itza.
It is believed to be a temple, or a place of sun worship.
This pyramid has a square base with nine terraces built upward.
Each terrace contains a set of 18 steps, which corresponds
to the 18 months of the Mayan Calendar. There are 91 stairs
on each side of the pyramid, totaling 364 steps. By adding
the platform to this figure, the total is 365 representing
the days in a solar year.
 Anasazi
Indians traveled from Mexico to present day northern New Mexico.
They used their knowledge to create calendars and great observatories.
At one time, Chaco Canyon was a huge center of trade and industry.
Chaco Canyon contains rocks recording stories about the sun.
One of the more famous ones is the Sun Dagger at Fajada Butte.
Fajada Butte is a shrine Anasazi
Indians traveled from Mexico to present day northern New Mexico.
They used their knowledge to create calendars and great observatories.
At one time, Chaco Canyon was a huge center of trade and industry.
Chaco Canyon contains rocks recording stories about the sun.
One of the more famous ones is the Sun Dagger at Fajada Butte.
Fajada Butte is a shrine  that contains two spiral petroglyphs. On the days close to
the summer solstice around the noon hour, a band of light
bisects the large spiral. Near the winter solstice around
the noon hour, two bands of light appear on either side of
the large spiral. During the spring and fall equinoxes, a
small band of light bisects the smaller spiral while a larger
dagger of light moves to the right of the center of the larger
spiral. that contains two spiral petroglyphs. On the days close to
the summer solstice around the noon hour, a band of light
bisects the large spiral. Near the winter solstice around
the noon hour, two bands of light appear on either side of
the large spiral. During the spring and fall equinoxes, a
small band of light bisects the smaller spiral while a larger
dagger of light moves to the right of the center of the larger
spiral.
 Hovenweep
Castle Hovenweep National Monument is located in southern
Utah in the United States. Hovenweep Castle, named after the
medieval castles that are found throughout Europe. One room
in the castle, known as the sun room, is the room that archaeoastronomers
believe the Anasazi used to mark equinoxes and solstices.
During the dates near the summer solstice, at sunset light
enters this room of the castle through a hole shining on a
threshold of a doorway. Likewise during the winter solstice
sunlight enters another hole and falls on the edge of another
doorway. It is believed that these people used this system
to determine planting dates and for priests to plan ceremonies. Hovenweep
Castle Hovenweep National Monument is located in southern
Utah in the United States. Hovenweep Castle, named after the
medieval castles that are found throughout Europe. One room
in the castle, known as the sun room, is the room that archaeoastronomers
believe the Anasazi used to mark equinoxes and solstices.
During the dates near the summer solstice, at sunset light
enters this room of the castle through a hole shining on a
threshold of a doorway. Likewise during the winter solstice
sunlight enters another hole and falls on the edge of another
doorway. It is believed that these people used this system
to determine planting dates and for priests to plan ceremonies.
 400
years ago, in Japan, people built a sun clock to use it as
a time piece.The sun clock at Kochi Castle, Japan is located
on the west entrance of the castle and one of many such time
pieces found throughout Japan. There is evidence that suggests
that this sun clock was influenced by the clepsydra (water
clock) used in China during the latter part of the seventh
century. The people of this time are presumed to have used
the sun clock as a way to standardize time in their communities.
People could walk up to the clock and estimate how much time
there was before or after the noon hour. Although the sun
clock is not precise in telling what time it is, it is more
precise than the previous ways of telling time. Earlier people
used the the position of the sun to tell the approximate time.
For example, if people were setting up a time to meet, they
might say that they would meet at a certain place when the
sun reached the tip of the horizon. 400
years ago, in Japan, people built a sun clock to use it as
a time piece.The sun clock at Kochi Castle, Japan is located
on the west entrance of the castle and one of many such time
pieces found throughout Japan. There is evidence that suggests
that this sun clock was influenced by the clepsydra (water
clock) used in China during the latter part of the seventh
century. The people of this time are presumed to have used
the sun clock as a way to standardize time in their communities.
People could walk up to the clock and estimate how much time
there was before or after the noon hour. Although the sun
clock is not precise in telling what time it is, it is more
precise than the previous ways of telling time. Earlier people
used the the position of the sun to tell the approximate time.
For example, if people were setting up a time to meet, they
might say that they would meet at a certain place when the
sun reached the tip of the horizon.
 So how
did ancient cultures know what time it was? So how
did ancient cultures know what time it was?
One
way of dividing up the day would be to observe the position
of the sun in the sky. Because of the rotation of the Earth,
the sun appears to move across the sky, rising in the east
and setting in the west. It is not safe to look at the sun,
so a simple device that used a shadow was developed to safely
observe the movement of the sun. The first sun dial was probably
just a stick that was put into the ground. At sunrise the
shadow of the stick was long and pointed toward the west.
During the morning the shadow would get shorter and by noon
it would be at its smallest length, perhaps pointing slightly
to the north in the Northern Hemisphere. After noon the shadow
would grow toward the east and as sunset approached it would
grow long once again. Sundials are the oldest known instrument
for telling time. They were probably invented in Egypt where
the day was divided into twelve equal hours as early as 6000
years ago. Sundials normally consist of a dial 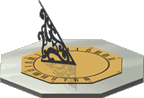 plane
(face) and gnomon (stick). The horizontal dial plane is marked
off into hours and quarter hours. The vertical gnomon, which
casts a shadow onto the dial plane, is usually triangular.
The angle of the gnomon is equal to the latitude of its location.
In the Northern Hemisphere the gnomon points to the north,
and in the Southern Hemisphere it points to the south. Of
course there are limitations to sundials. It is difficult
or impossible to use a sundial on a cloudy day or at night.
They are still used today as decorative pieces in many outdoor
locations, including gardens and parks. plane
(face) and gnomon (stick). The horizontal dial plane is marked
off into hours and quarter hours. The vertical gnomon, which
casts a shadow onto the dial plane, is usually triangular.
The angle of the gnomon is equal to the latitude of its location.
In the Northern Hemisphere the gnomon points to the north,
and in the Southern Hemisphere it points to the south. Of
course there are limitations to sundials. It is difficult
or impossible to use a sundial on a cloudy day or at night.
They are still used today as decorative pieces in many outdoor
locations, including gardens and parks.

 We've
been all over the world, visiting places and viewing artifacts
of ancient people who observed the sun. We know this by the
artifacts that they left behind. But are there other ways
that ancient people interacted with the sun? Of course! Ancient
Greeks and Romans explained the sun with mythology while others explained it with cultural stories. Learn
more about stories of origins, mythology, and the sun here. We've
been all over the world, visiting places and viewing artifacts
of ancient people who observed the sun. We know this by the
artifacts that they left behind. But are there other ways
that ancient people interacted with the sun? Of course! Ancient
Greeks and Romans explained the sun with mythology while others explained it with cultural stories. Learn
more about stories of origins, mythology, and the sun here.
|
