Basics of Spaceflight: Glossary
Use your browser's "FIND" capability to locate a word right away on this page. You should also have a good English dictionary at hand. Additional resources are the "SEARCH BSF" function at the bottom of each page, and the Units of Measure section. You might also wish to consult the SEDS Basic Astronomical Terms page, or the NASA Thesaurus. Some additional glossaries that may be useful are linked here.
A
a, A -- Acceleration. a = Δ velocity / Δ time. Acceleration = Force / Mass
A -- Ampere, the SI base unit of electric current.
Å -- Angstrom (0.0001 micrometer, 0.1 nm).
A Ring -- The outermost of the three rings of Saturn that are easily seen in a small telescope.
AAAS -- American Association for the Advancement of Science.
AACS -- Attitude and Articulation Control Subsystem onboard a spacecraft.
AAS -- American Astronomical Society.
AC -- Alternating current.
Acceleration -- Change in velocity. Note that since velocity comprises both direction and magnitude (speed), a change in either direction or speed constitutes acceleration.
ALT -- Altitude.
ALT -- Altimetry data.
AM -- Ante meridiem (Latin: before midday), morning.
am -- Attometer (10-18 m).
AMMOS -- Advanced Multimission Operations System.
Amor -- A class of Earth-crossing asteroid.
AO -- Announcement of Opportunity.
AOS -- Acquisition Of Signal, used in DSN operations.
Aphelion -- Apoapsis in solar orbit.
Apoapsis -- The farthest point in an orbit from the body being orbited.
Apogee -- Apoapsis in Earth orbit.
Apochron -- Apoapsis in Saturn orbit.
Apojove -- Apoapsis in Jupiter orbit.
Apollo -- A class of Earth-crossing asteroid.
Apolune -- Apoapsis in lunar orbit.
Apselene -- Apoapsis in lunar orbit.
Argument -- Angular distance.
Argument of periapsis -- The argument (angular distance) of periapsis from the ascending node.
Ascending node -- The point at which an orbit crosses a reference plane (such as a planet's equatorial plane or the ecliptic plane) going north.
Asteroids -- Small bodies composed of rock and metal in orbit about the Sun.
Aten -- A class of Earth-crossing asteroid.
Attometer -- 10-18 meter.
Astronomical Twilight -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
au -- Astronomical Unit, based on the mean Earth-to-Sun distance, 149,597,870 km. Refer to "Units of Measure" section for complete information.
AZ -- Azimuth.
B
B -- Bel, a unit of ratio equal to ten decibels. Named in honor of telecommunications pioneer Alexander Graham Bell.
B Ring -- The middle of the three rings of Saturn that are easily seen in a small telescope.
Barycenter -- The common center of mass about which two or more bodies revolve.
Beacon -- Downlink from a spacecraft that immediately indicates the state of the spacecraft as being one of several possible states by virtue of the presence and/or frequency of the subcarrier. See Chapter 10.
Bel -- Unit of ratio equal to ten decibels. Named in honor of telecommunications pioneer Alexander Graham Bell.
Billion -- In the U.S., 109. In other countries using SI, 1012.
Bi-phase -- A modulation scheme in which data symbols are represented by a shift from one phase to another. See Chapter 10.
BOT -- Beginning Of Track, used in DSN operations.
BPS -- Bits Per Second, same as Baud rate.
BSF -- Basics of Space Flight (this document).
BVR -- DSN Block Five (V) Receiver.
BWG -- Beam waveguide 34-m DSS, the DSN's newest DSS design.
C
c -- The speed of light, 299,792 km per second.
C-band -- A range of microwave radio frequencies in the neighborhood of 4 to 8 GHz.
C Ring -- The innermost of the three rings of Saturn that are easily seen in a small telescope.
Caltech -- The California Institute of Technology.
Carrier -- The main frequency of a radio signal
generated by a transmitter prior to application of any modulation.
Cassegrain -- Reflecting scheme in antennas and telescopes having a primary and a secondary reflecting surface to "fold" the EMF back to a focus near the primary reflector.
CCD -- Charge Coupled Device, a solid-state imaging detector.
C&DH -- Command and Data Handling subsystem on board a spacecraft, similar to CDS.
CCS -- Computer Command subsystem on board a spacecraft, similar to CDS.
CCSDS -- Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems, developer of standards for spacecraft uplink and downlink, including packets.
CDR -- GCF central data recorder.
CDS -- Command and Data Subsystem onboard a spacecraft.
CDSCC -- DSN's Canberra Deep Space Communications Complex in Australia.
CDU -- Command Detector Unit onboard a spacecraft.
Centrifugal force -- The outward-tending apparent force of a body revolving around another body.
Centimeter -- 10-2 meter.
Centripetal acceleration -- The inward acceleration of a body revolving around another body.
CGPM -- General Conference of Weights and Measures, Sevres France. The abbreviation is from the French. CGPM is the source for the multiplier names (kilo, mega, giga, etc.) listed in this document.
Chandler wobble -- A small motion in the Earth's rotation axis relative to the surface, discovered by American astronomer Seth Carlo Chandler in 1891. Its amplitude is about 0.7 arcseconds (about 15 meters on the surface) with a period of 433 days. It combines with another wobble with a period of one year, so the total polar motion varies with a period of about 7 years. The Chandler wobble is an example of free nutation for a spinning non-spherical object.
Channel -- In telemetry, one particular measurement to which changing values may be assigned. See Chapter 10.
CIT -- California Institute of Technology, Caltech.
Civil Twilight -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
Clarke orbit -- Geostationary orbit.
CMC -- Complex Monitor and Control, a subsystem at DSCCs.
CMD -- DSN Command System. Also, Command data.
CNES -- Centre National d'Études Spatiales, France.
Conjunction -- A configuration in which two celestial bodies have their least apparent separation.
Coherent -- Two-way communications mode wherein the spacecraft generates its downlink frequency based upon the frequency of the uplink it receives.
Coma -- The cloud of diffuse material surrounding the nucleus of a comet.
Comets -- Small bodies composed of ice and rock in various orbits about the Sun.
CRAF -- Comet Rendezvous / Asteroid Flyby mission, cancelled.
CRS -- Cosmic Ray Subsystem, high-energy particle instrument on Voyager.
CRT -- Cathode ray tube video display device.
D
DC -- Direct current.
DC -- The DSN Downlink Channel, several of which are in each DSN Downlink Tracking & Telemetry subsystem, DTT.
DCC -- The DSN Downlink Channel Controller, one of which is in each DSN Downlink Channel, DC.
DCPC -- The DSN Downlink Channel Processor Cabinet, one of which contains a DSN Downlink Channel, DC.
DEC -- Declination.
Decibel -- dB, an expression of ratio (see dB, above). One tenth of a Bel. See NIST website for further definition.
Declination -- The measure of a celestial body's apparent height above or below the celestial equator.
Density -- Mass per unit volume. For example, the density of water can be stated as 1 gram/cm3.
Descending node -- The point at which an orbit crosses a reference plane (such as a planet's equatorial plane or the ecliptic plane) going south.
DKF -- DSN keyword file, also known as KWF.
Doppler effect -- The effect on frequency imposed by relative motion between transmitter and receiver. See Chapter 6.
Downlink -- Signal received from a spacecraft.
DSOT -- Data System Operations Team, part of the DSMS staff.
DSCC -- Deep Space Communications Complex, one of three DSN tracking sites at Goldstone, California; Madrid, Spain; and Canberra, Australia; spaced about equally around the Earth for continuous tracking of deep-space vehicles.
DSMS -- Deep Space Mission System, the system of computers, software, networks, and procedures that processes data from the DSN at JPL.
DSN -- Deep Space Network, NASA's worldwide spacecraft tracking facility managed and operated by JPL.
DSS -- Deep Space Station, the antenna and front-end equipment at DSCCs.
DT -- Dynamical Time. Replaces Ephemeris Time, ET, as the independent argument in dynamical theories and ephemerides. Its unit of duration is based on the orbital motions of the Earth, Moon, and planets. DT has two expressions, Terrestrial Time, TT, (or Terrestrial Dynamical Time, TDT), and Barycentric Dynamical Time, TDB. More information on these, and still more timekeeping expressions, may be found at the U.S. Naval Observatory website.
DTT -- The DSN Downlink Tracking & Telemetry subsystem.
Dyne -- A unit of force equal to the force required to accelerate a 1-g mass 1 cm per second per second. Compare with Newton.
E
E -- Exa, a multiplier, x1018 from the Greek "hex" (six, the "h" is dropped). The reference to six is because this is the sixth multiplier in the series k, M, G, T, P, E. See the entry for CGPM.
Earth -- Third planet from the Sun, a terrestrial planet.
Eccentricity -- The distance between the foci of an ellipse divided by the major axis.
Ecliptic -- The plane in which Earth orbits the Sun and in which solar and lunar eclipses occur.
EDL -- (Atmospheric) Entry, Descent, and Landing.
EDR -- Experiment Data Record.
EHz -- ExaHertz (1018 Hz)
EL -- Elevation.
Ellipse -- A closed plane curve generated in such a way that the sums of its distances from the two fixed points (the foci) is constant.
ELV -- Expendable launch vehicle.
EM -- Electromagnetic.
EMF -- Electromagnetic force (radiation).
EMR -- Electromagnetic radiation.
EOT -- End Of Track, used in DSN operations.
Equator -- An imaginary circle around a body which is everywhere equidistant from the poles, defining the boundary between the northern and southern hemispheres.
Equinox -- The equinoxes are times at which the center of the Sun is directly above the Earth's equator. The day and night would be of equal length at that time, if the Sun were a point and not a disc, and if there were no atmospheric refraction. Given the apparent disc of the Sun, and the Earth's atmospheric refraction, day and night actually become equal at a point within a few days of each equinox. The vernal equinox marks the beginning of spring in the northern hemisphere, and the autumnal equinox marks the beginning of autumn in the northern hemisphere.
ERC -- NASA's Educator Resource Centers.
ERT -- Earth-received time, UTC of an event at DSN receive-time, equal to SCET plus OWLT.
ESA -- European Space Agency.
ESP -- Extra-Solar Planet, a planet orbiting a star other than the Sun. See also Exoplanet.
ET -- Ephemeris time, a measurement of time defined by orbital motions. Equates to Mean Solar Time corrected for irregularities in Earth's motions. Obsolete, replaced by TT, Terrestrial Time.
eV -- Electron volt, a measure of the energy of subatomic particles.
Exoplanet -- Extrasolar planet. A planet orbiting a star other than the Sun.
Extrasolar planet -- A planet orbiting a star other than our Sun. Exoplanet.
F
FDS -- Flight Data Subsystem.
FE -- Far Encounter phase of mission operations.
Femtometer -- 10-15 meter.
Fluorescence -- The phenomenon of emitting light upon
absorbing radiation of an invisible wavelength.
fm -- Femtometer (10-15 m)
FM -- Frequency modulation.
FTS -- DSN Frequency and Timing System. Also, frequency and timing data.
FY -- Fiscal year.
G
G -- Universal Constant of Gravitation. Its tiny value (G = 6.6726 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2) is unchanging throughout the universe.
G -- Giga, a multiplier, x109, from the Latin "gigas" (giant). See the entry for CGPM.
g -- Acceleration due to a body's gravity. Constant at any given place, the value of g varies from object to object (e.g. planets), and also with the distance from the center of the object. The relationship between the two constants is: g = GM/r2 where r is the radius of separation between the masses' centers, and M is the mass of the primary body (e.g. a planet). At Earth's surface, the value of g = 9.8 meters per second per second (9.8m/s2). See also weight.
g -- Gram, a thousandth of the metric standard unit of mass (see kg). The gram was originally based upon
the weight of a cubic centimeter of water, which still approximates the current value.
Gal -- Unit of gravity field measurement corresponding to a gravitational acceleration of 1 cm/sec2.
Galaxy -- One of billions of systems, each composed of numerous stars, nebulae, and dust.
Galilean satellites -- The four large satellites of Jupiter so named because Galileo discovered them when he turned his telescope toward Jupiter: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto.
Gamma rays -- Electromagnetic radiation in the neighborhood of 100 femtometers wavelength.
GCF -- Ground Communications Facilities, provides data and voice communications between JPL and the three DSCCs.
GDS -- Ground Data System, encompasses DSN, GCF, DSMS, and project data processing systems.
GDSCC -- DSN's Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex in California.
GEO -- Geosynchronous Earth Orbit.
Geostationary -- A geosynchronous equatorial circular orbit. Also called Clarke orbit.
Geosynchronous -- A direct, circular, low inclination orbit about the Earth having a period of 23 hours 56 minutes 4 seconds.
GHz -- Gigahertz (109 Hz).
GLL -- The Galileo spacecraft.
GMT -- Greenwich Mean Time. Obsolete. UT, Universal Time is preferred.
Gravitation -- The mutual attraction of all masses in the
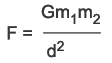
universe. Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation holds that every two bodies attract each other with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses, and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. This relation is given by the formula shown here, where F is the force of attraction between the two objects, given G the Universal Constant of Gravitation, masses m1 and m2, and d distance. Also stated as Fg = GMm/r2 where Fg is the force of gravitational attraction, M the larger of the two masses, m the smaller mass, and r the radius of separation of the centers of the masses. See also weight.
Gravitational waves -- Einsteinian distortions of the space-time medium predicted by general relativity theory (not yet directly detected as of March 2010). (Not to be confused with gravity waves, see below.)
Gravity assist -- Technique whereby a spacecraft takes angular momentum from a planet's solar orbit (or a satellite's orbit) to accelerate the spacecraft, or the reverse. See Chapter 4.
Gravity waves -- Certain dynamical features in a planet's atmosphere (not to be confused with gravitational waves, see above).
Great circle -- An imaginary circle on the surface of a sphere whose center is at the center of the sphere.
GSSR -- Goldstone Solar System Radar, a technique which uses very high-power X and S-band transmitters at DSS 14 to illuminate solar system objects for imaging.
GTL -- Geotail spacecraft.
GTO -- Geostationary (or geosynchronous) Transfer Orbit.
H
HA -- Hour Angle.
Halo orbit -- A spacecraft's pattern of controlled drift about an unstable Lagrange point (L1 or L2 for example) while in orbit about the primary body (e.g. the Sun).
HEF -- DSN's high-efficiency 34-m DSS, replaces STD DSSs.
Heliocentric -- Sun-centered.
Heliopause -- The boundary theorized to be roughly circular or teardrop-shaped, marking the edge of the Sun's
influence, perhaps 100 AU from the Sun.
Heliosphere -- The space within the boundary of the heliopause, containing the Sun and solar system.
HEMT -- High-electron-mobility transistor, a low-noise amplifier used in DSN.
HGA -- High-Gain Antenna onboard a spacecraft.
Hohmann Transfer Orbit -- Interplanetary trajectory using the least amount of propulsive energy. See Chapter 4.
Horizon -- The line marking the apparent junction of Earth and sky. For the technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory's Astronomical Applications.
h -- Hour, 60 minutes of time.
Hour Angle -- The angular distance of a celestial object measured westward along the celestial equator from the
zenith crossing. In effect, HA represents the RA for a particular location and time of day.
I
ICRF -- International Celestial Reference Frame. The realization of the ICRS provided by the adopted positions of extragalactic objects. Link.
ICRS -- International Celestial Reference System. Conceptual basis for celestial positions, aligned with respect to extremely distant objects and utilizing the theory of general relativity. Link.
IERS -- International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service. Link.
IF -- Intermediate Frequency. In a radio system, a selected processing frequency between RF (Radio Frequency) and the end product (e.g. audio frequency).
Inclination -- The angular distance of the orbital plane from the plane of the planet's equator, stated in degrees.
IND -- JPL's Interplanetary Network Directorate, formerly IPN-ISD.
Inferior planet -- Planet which orbits closer to the
Sun than the Earth's orbit.
Inferior conjunction -- Alignment of Earth, Sun, and an inferior planet on the same side of the Sun.
Ion -- A charged particle consisting of an atom stripped of one or more of its electrons.
IPAC -- Infrared Processing and Analysis Center at Caltech campus on Wilson Avenue in Pasadena.
IPC -- Information Processing Center, JPL's computing center on Woodbury Avenue in Pasadena.
IPN-ISD -- (Obsolete. See IND) JPL's Interplanetary Network and Information Systems Directorate, formerly TMOD.
IR -- Infrared, meaning "below red" radiation. Electromagnetic radiation in the neighborhood of 100 micrometers
wavelength.
IRAS -- Infrared Astronomical Satellite.
ISM -- Interstellas medium.
ISO -- International Standards Organization.
ISOE -- Integrated Sequence of Events.
Isotropic -- Having uniform properties in all directions.
IUS -- Inertial Upper Stage.
J
JGR -- Journal Of Geophysical Research.
Jovian -- Jupiter-like planets, the gas giants Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
JPL -- Jet Propulsion Laboratory, operating division of the California Institute of Technology.
Jupiter -- Fifth planet from the Sun, a gas giant or Jovian planet.
K
K -- Kelvin, the SI base unit of thermodynamic temperature.
K-band -- A range of microwave radio frequencies in the neighborhood of 12 to 40 GHz.
kg -- Kilogram. See below.
Keyhole -- An area in the sky where an antenna cannot track a spacecraft because the required angular rates would be too high. Mechanical limitations may also contribute to keyhole size. Discussed in depth under Chapter 2.
kHz -- kilohertz.
Kilogram (kg) -- the SI base unit of mass, based on the mass of a metal cylinder kept in France. See also g (gram).
Kilometer -- 103 meter.
Klystron -- A microwave travelling wave tube power amplifier used in transmitters.
km -- Kilometers.
KSC -- Kennedy Space Center, Cape Canaveral, Florida.
KWF -- Keyword file of events listing DSN station
activity. Also known as DKF, DSN keyword file.
Kuiper belt -- A disk-shaped region about 30 to 100 AU from the Sun considered to be the source of the short-period comets.
L
LAN -- Local area network for inter-computer communications.
Large Magellanic Cloud -- LMC, the larger of two small galaxies orbiting nearby our Milky Way galaxy, which are
visible from the southern hemisphere.
Laser -- Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Compare with Maser.
Latitude -- Circles in parallel planes to that of the equator defining north-south measurements, also called parallels.
L-band -- A range of microwave radio frequencies in the neighborhood of 1 to 2 GHz.
LCP -- Left-hand circular polarization.
Leap Second -- A second which may be added or subtracted to adjust UTC at either, both, or neither, of two specific opportunities each year.
Leap Year -- Every fourth year, in which a 366th day is added since the Earth's revolution takes 365 days 5 hr 49 min.
LECP -- Low-Energy Charged-Particular Detector onboard a spacecraft.
LEO -- Low Equatorial Orbit.
LGA -- Low-Gain Antenna onboard a spacecraft.
Light -- Electromagnetic radiation in the neighborhood of 1 nanometer wavelength.
Light speed -- 299,792 km per second, the constant c.
Light time -- The amount of time it takes light or radio signals to travel a certain distance at light speed.
Light year -- A measure of distance, the distance light travels in one year, about 63,197 au.
LMC -- Large Magellanic Cloud, the larger of two small galaxies orbiting nearby our Milky Way galaxy, which are visible from the southern hemisphere.
LMC -- Link Monitor and Control subsystem at the SPCs within the DSN DSCCs.
LNA -- Low-noise amplifier in DSN, either a maser or a HEMT.
Local time -- Time adjusted for location around the Earth or other planets in time zones.
Longitude -- Great circles that pass through both the north and south poles, also called meridians.
LOS -- Loss Of Signal, used in DSN operations.
LOX -- Liquid oxygen.
M
m -- Meter (U.S. spelling; elsewhere metre), the international standard of linear measurement.
m -- milli- multiplier of one one-thousandth, e.g. 1 mW = 1/1000 of a Watt, mm = 1/1000 meter.
m, M -- Mass. The kilogram is the standard unit of mass. Mass = Acceleration / Force.
M -- Mega, a multiplier, x106 (million) from the Greek "megas" (great). See the entry for CGPM.
M100 -- Messier Catalog entry number 100 is a spiral galaxy in the Virgo cluster seen face-on from our solar system.
Major axis -- The maximum diameter of an ellipse.
Mars -- Fourth planet from the Sun, a terrestrial planet.
Maser -- A microwave travelling wave tube amplifier named for its process of Microwave Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Compare with Laser. In the Deep Space Network, masers are used as low-noise amplifiers of downlink signals, and also as frequency standards.
Mass -- A fundamental property of an object comprising a numerical measure of its inertia; the amount of matter in the object. While an object's mass is constant (ignoring Relativity for this purpose), its weight will vary depending on its location. Mass can only be measured in conjunction with force and acceleration.
MC-cubed -- Mission Control and Computing Center at JPL (outdated).
MCCC -- Mission Control and Computing Center at JPL (outdated).
MCD -- DSN's maximum-likelihood convolutional decoder, the Viterbi decoder.
MCT -- Mission Control Team, JPL Section 368 mission execution real-time operations.
MDSCC -- DSN's Madrid Deep Space Communications Complex in Spain.
Mean solar time -- Time based on an average of the variations caused by Earth's non-circular orbit. The 24-hour day is based on mean solar time.
Mercury -- First planet from the Sun, a terrestrial planet.
Meridians -- Great circles that pass through both the north and south poles, also called lines of longitude.
MESUR -- The Mars Environmental Survey project at JPL, the engineering prototype of which was originally called MESUR Pathfinder, later Mars Pathfinder.
Meteor -- A meteoroid which is in the process of entering Earth's atmosphere. It is called a meteorite after landing.
Meteorite -- Rocky or metallic material which has fallen to Earth or to another planet.
Meteoroid -- Small bodies in orbit about the Sun which are candidates for falling to Earth or to another planet.
MGA -- Medium-Gain Antenna onboard a spacecraft.
MGN -- The Magellan spacecraft.
MGSO -- (Obsolete. See TMOD) JPL's Multi-mission Ground Systems Office.
MHz -- Megahertz (106 Hz).
Micrometer -- µm, 10-6 meter.
Micron -- Obsolete terms for micrometer, µm (10-6 m).
Milky Way -- The galaxy which includes the Sun and Earth.
Millimeter -- 10-3 meter.
MIT -- Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
MLI -- Multi-layer insulation (spacecraft blanketing). See Chapter 11.
mm -- millimeter (10-3 m).
MO -- The Mars Observer spacecraft.
Modulation -- The process of modifying a radio frequency by shifting its phase, frequency, or amplitude to carry
information.
MON -- DSN Monitor System. Also, monitor data.
Moon -- A small natural body which orbits a larger one.
A natural satellite. Capitalized, the Earth's natural satellite.
Moonrise -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
Moonset -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
MOSO -- Multimission Operations Systems Office at JPL.
MR -- Mars relay.
µm -- Micrometer (10-6 m).
Multiplexing -- A scheme for delivering many different measurements in one data stream. See Chapter 10.
N
N -- Newton, the SI unit of force equal to that required to accelerate a 1-kg mass 1 m per second per second
(1m/sec2). Compare with dyne.
N -- North.
Nadir -- The direction from a spacecraft directly down toward the center of a planet. Opposite the zenith.
NASA -- National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
Nautical Twilight -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
NE -- Near Encounter phase in flyby mission operations.
Neptune -- Eighth planet from the Sun, a gas giant or Jovian planet.
NiCad -- Nickel-cadmium rechargable battery.
NIMS -- Near-Infrared Mapping Spectrometer onboard the Galileo spacecraft.
NIST -- National Institute of Standards.
nm -- Nanometer (10-9 m).
nm -- Nautical Mile, equal to the distance spanned by one minute of arc in latitude, 1.852 km.
NMC -- Network Monitor and Control subsystem in DSN.
NOCC -- DSN Network Operations Control Center at JPL.
Nodes -- Points where an orbit crosses a reference plane.
Non-coherent -- Communications mode wherein a spacecraft generates its downlink frequency independent of any uplink frequency.
Nucleus -- The central body of a comet.
Nutation -- A small nodding motion in a rotating body. Earth's nutation has a period of 18.6 years and an amplitude of 9.2 arc seconds.
NRZ -- Non-return to zero. Modulation scheme in which a phase deviation is held for a period of time in order to represent a data symbol. See Chapter 10.
NSP -- DSN Network Simplification Project. A project that re-engineered the DSN to consolidate seven data systems into two data systems that handle the same data types.
OB -- Observatory phase in flyby mission operations encounter period.
One-way -- Communications mode consisting only of downlink received from a spacecraft.
Oort cloud -- A large number of comets theorized to orbit the Sun in the neighborhood of 50,000 au.
OPCT -- Operations Planning and Control Team at JPL, "OPSCON." Obsolete, replaced by DSOT, Data Systems Operations Team.
Opposition -- Configuration in which one celestial body is opposite another in the sky. A planet is in opposition when it is 180 degrees away from the Sun as viewed from another planet (such as Earth). For example, Saturn is at opposition when it is directly overhead at midnight on Earth.
OPNAV -- Optical Navigation (images).
OSI -- ISO's Open Systems Interconnection protocol suite.
OSR -- Optical Solar Reflector, thermal control component onboard a spacecraft.
OSS -- Office Of Space Science, NASA. Obsolete, replaced by Science Mission Directorate (SMD).
OSSA -- Office Of Space Science and Applications, NASA (Obsolete, see OSS).
OTM -- Orbit Trim Maneuver, spacecraft propulsive maneuver.
OWLT -- One-Way Light Time, elapsed time between Earth and spacecraft or solar system body.
P
Packet -- A quantity of data used as the basis for multiplexing, for example in accordance with CCSDS.
PAM -- Payload Assist Module upper stage.
Parallels -- Circles in parallel planes to that of the equator defining north-south measurements, also called lines of latitude.
Pathfinder -- The Mars Environmental Survey (MESUR) engineering prototype later named Mars Pathfinder.
PDS -- Planetary Data System.
PDT -- Pacific Daylight Time.
PE -- Post Encounter phase in flyby mission operations.
Periapsis -- The point in an orbit closest to the body being orbited.
Perigee -- Periapsis in Earth orbit.
Perichron -- Periapsis in Saturn orbit.
Perihelion -- Periapsis in solar orbit.
Perijove -- Periapsis in Jupiter orbit.
Perilune -- Periapsis in lunar orbit.
Periselene -- Periapsis in lunar orbit.
Phase -- The angular distance between peaks or troughs of two waveforms of similar frequency.
Phase -- The particular appearance of a body's state of illumination, such as the full or crescent phases of the Moon.
Phase -- Any one of several predefined periods in a mission or other activity.
Photovoltaic -- Materials that convert light into
electric current.
PHz -- Petahertz (1015 Hz).
PI -- Principal Investigator, scientist in charge of an experiment.
Picometer -- 10-12 meter.
PIO -- JPL's Public Information Office.
Plasma -- Electrically conductive fourth state of matter (other than solid, liquid, or gas), consisting of ions and
electrons.
PLL -- Phase-lock-loop circuitry in telecommunications technology.
Plunge -- In describing the tracking motion of an AZ-EL or ALT-AZ mounted radio telescope, to "plunge" means to exceed 90° in elevation and then to continue tracking as elevation decreases on the other side without swiveling around in azimuth. This is not a capability of DSN antennas.
Pluto -- Ninth planet from the Sun, sometimes
classified as a small terrestrial planet.
pm -- Picometer (10-12 m).
PM -- Post meridiem (Latin: after midday), afternoon.
PN10 -- Pioneer 10 spacecraft.
PN11 -- Pioneer 11 spacecraft.
Prograde -- Orbit in which the spacecraft moves in the same direction as the planet rotates. See retrograde.
PST -- Pacific Standard Time.
PSU -- Pyrotechnic Switching Unit onboard a spacecraft.
Q
Quasar -- Quasi-stellar object observed mainly in radio waves. Quasars are extragalactic objects believed to be the very distant centers of active galaxies.
R
Radian -- Unit of angular measurement equal to the angle at the center of a circle subtended by an arc equal in
length to the radius. Equals about 57.296 degrees.
RAM -- Random Access Memory.
RCP -- Right-hand circular polarization.
Red dwarf -- A small star, on the order of 100 times the mass of Jupiter.
Reflection -- The deflection or bouncing of electromagnetic waves when they encounter a surface.
Refraction -- The deflection or bending of electromagnetic waves when they pass from one kind of transparent
medium into another.
REM -- Receiver Equipment Monitor within the Downlink Channel (DC) of the Downlink Tracking & Telemetry subsystem (DTT).
Retrograde -- Orbit in which the spacecraft moves in the opposite direction from the planet's rotation. See prograde.
RF -- Radio Frequency.
RFI -- Radio Frequency Interference.
Right Ascension -- The angular distance of a celestial object measured in hours, minutes, and seconds along the
celestial equator eastward from the vernal equinox.
Rise -- As in ascending above the horizon, for the technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory's Astronomical Applications.
RNS -- GCF reliable network service.
ROM -- Read Only Memory.
RPIF -- Regional Planetary Imaging Data Facilities.
RRP -- DSN Receiver & Ranging Processor within the Downlink Channel (DC) of the Downlink Tracking & Telemetry subsystem (DTT).
RS -- DSN Radio Science System. Also, radio science data.
RTG -- Radioisotope Thermo-Electric Generator onboard a spacecraft.
RTLT -- Round-Trip Light Time, elapsed time roughly equal to 2 x OWLT.
S
S -- South.
s -- Second, the SI base unit of time (see this extensive definition).
SA -- Solar Array, photovoltaic panels onboard a spacecraft.
SAF -- Spacecraft Assembly Facility, JPL Building 179.
SAR -- Synthetic Aperture Radar
Satellite -- A small body which orbits a larger one. A natural or an artificial moon. Earth-orbiting spacecraft are called satellites. While deep-space vehicles are technically satellites of the Sun or of another planet, or of the galactic center, they are generally called spacecraft instead of satellites.
Saturn -- Sixth planet from the Sun, a gas giant or Jovian planet.
S-band -- A range of microwave radio frequencies in the neighborhood of 2 to 4 GHz.
SC -- Steering Committee.
SCET -- Spacecraft Event Time, equal to ERT minus OWLT.
SCLK -- Spacecraft Clock Time, a counter onboard a spacecraft.
Sec -- Abbreviation for Second.
Second -- the SI base unit of time. See this extensive definition.
SEDR -- Supplementary Experiment Data Record.
SEF -- Spacecraft event file.
SEGS -- Sequence of Events Generation Subsystem.
Semi-major axis -- Half the distance of an ellipse's maximum diameter, the distance from the center of the ellipse to one end.
Set -- As in going below the horizon, for the technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory's Astronomical Applications.
SFOF -- Space Flight Operations Facility, Buildings 230 and 264 at JPL.
SFOS -- Space Flight Operations Schedule, product of SEGS.
Shepherd moons -- Moons which gravitationally confine ring particles.
SI -- The International System of Units (metric system). See also Units of Measure.
SI base unit -- One of seven SI units of measure from which all the other SI units are derived. See SI derived unit. See also Units of Measure.
SI derived unit -- One of many SI units of measure expressed as relationships of the SI base units. For example, the watt, W, is the SI derived unit of power. It is equal to joules per second. W = m2 ⋅ kg ⋅ s–3 (Note: the joule, J, is the SI derived unit for energy, work, or quantity of heat.) See also Units of Measure.
Sidereal time -- Time relative to the stars other than the Sun.
SIRTF -- Space Infrared Telescope Facility.
SMC -- Small Magellanic Cloud, the smaller of two small galaxies orbiting nearby our Milky Way galaxy, which are
visible from the southern hemisphere.
SMD -- Science Mission Directorate, NASA (previously Office Of Space Science, OSS).
SOE -- Sequence of Events.
Solar wind -- Flow of lightweight ions and electrons
(which together comprise plasma) thrown from the Sun.
SNR -- Signal-to-Noise Ratio.
SPC -- Signal Processing Center at each DSCC.
Specific Impulse -- A measurement of a rocket's relative performance. Expressed in seconds, the number of which a rocket can produce one pound of thrust from one pound of fuel. The higher the specific impulse, the less fuel required to produce a given amount of thrust.
Spectrum -- A range of frequencies or wavelengths.
SSA -- Solid State Amplifier in a spacecraft telecommunications subsystem, the final stage of amplification for
downlink.
SSI -- Solid State Imaging Subsystem, the CCD-based cameras on Galileo.
SSI -- Space Services, Inc., Houston, manufacturers of the Conestoga launch vehicle.
STD -- Standard 34-m DSS, retired from DSN service.
STS -- Space Transportation System (Space Shuttle).
Subcarrier -- Modulation applied to a carrier which is itself modulated with information-carrying variations.
Sunrise -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
Sunset -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
Sun synchronous orbit -- A spacecraft orbit that precesses, wherein the location of periapsis changes with respect to the planet's surface so as to keep the periapsis location near the same local time on the planet each orbit. See walking orbit.
Superior planet -- Planet which orbits farther from the Sun than Earth's orbit.
Superior conjunction -- Alignment between Earth and a planet on the far side of the Sun.
SWG -- Science Working Group.
T
TAU -- Thousand AU Mission.
TCM -- Trajectory Correction Maneuver, spacecraft propulsive maneuver.
TDM -- Time-division multiplexing.
Termination shock -- Shock at which the solar wind is
thought to slow to subsonic speed, well inside the heleopause.
T -- Tera, a multiplier x1012, from the Greek teras (monster). See the entry for CGPM.
Terrestrial planet -- One of the four inner Earth-like planets.
Three-way -- Coherent communications mode wherein a DSS receives a downlink whose frequency is based upon the frequency of an uplink provided by another DSS.
TMOD -- (Obsolete. See IPN-ISD) JPL's Telecommunications and Mission Operations Directorate. Formerly MGSO.
THz -- Terahertz (1012 Hz).
TLM -- DSN Telemetry data.
TLP -- DSN Telemetry Processor within the DTT Downlink Channel.
TOS -- Transfer Orbit Stage, upper stage.
Transducer -- Device for changing one kind of energy into another, typically from heat, position, or pressure into a
varying electrical voltage or vice-versa, such as a microphone or speaker.
Transit -- The transit time of a celestial body refers to the instant that its center crosses an imaginary line in the sky - the observer's meridian - running from north to south. For a more detailed explanation, visit the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
Transponder -- Electronic device which combines a transmitter and a receiver.
TRC -- NASA's Teacher Resource Centers. Obsolete, now called Educator Resource Centers, ERC.
TRK -- DSN Tracking System. Also, Tracking data.
TRM -- Transmission Time, UTC Earth time of uplink.
True anomaly -- The angular distance of a point in an orbit past the point of periapsis, measured in degrees.
Twilight -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
TWNC -- Two-Way Non-Coherent mode, in which a spacecraft's downlink is not based upon a received uplink from
DSN.
Two-way -- Communications mode consisting of downlink received from a spacecraft while uplink is being received at the spacecraft. See also coherent.
TWT -- Traveling Wave Tube, downlink power amplifier in a spacecraft telecommunications subsystem, the final stage of amplification for downlink (same unit as TWTA).
TWTA -- Traveling Wave Tube Amplifier, downlink power amplifier in a spacecraft telecommunications subsystem, the final stage of amplification for downlink (same unit as TWT).
TXR -- DSN's DSCC Transmitter assembly.
U
µm -- Micrometer (10-6 m).
ULS -- Ulysses spacecraft.
Uplink -- Signal sent to a spacecraft.
UPL -- The DSN Uplink Tracking & Command subsystem.
Uranus -- Seventh planet from the Sun, a gas giant or Jovian planet.
USO -- Ultra Stable Oscillator, in a spacecraft telecommunications subsystem.
UT -- Universal Time, also called Zulu (Z) time, previously Greenwich Mean Time. UT is based on the imaginary "mean Sun," which averages out the effects on the length of the solar day caused by Earth's slightly non-circular orbit about the Sun. UT is not updated with leap seconds as is UTC.
UTC -- Coordinated Universal Time, the world-wide scientific standard of timekeeping. It is based upon carefully maintained atomic clocks and is highly stable. Its rate does not change by more than about 100 picoseconds per day. The addition or subtraction of leap seconds, as necessary, at two opportunities every year adjusts UTC for irregularities in Earth's rotation. The U.S. Naval Observatory website provides information in depth on the derivation of UTC.
UV -- Ultraviolet (meaning "above violet") radiation. Electromagnetic radiation in the neighborhood of 100 nanometers wavelength.
UWV -- DSN Microwave subsystem in DSSs which includes waveguides, waveguide switches, LNAs, polarization filters, etc.
V
Velocity -- A vector quantity whose magnitude is a body's speed and whose direction is the body's direction of motion.
Venus -- Second planet from the Sun, a terrestrial planet.
VGR1 -- Voyager 1 spacecraft.
VGR2 -- Voyager 2 spacecraft.
VLBI -- DSN Very Long Baseline Interferometry System. Also, VLBI data. Link.
W
W -- Watt, a measure of electrical power equal to potential in volts times current in amps.
W -- West.
Walking orbit -- A spacecraft orbit that precesses, wherein the location of periapsis changes with respect to the planet's surface in a useful way. See Sun-synchronous.
Wavelength -- The distance that a wave from a single oscillation of electromagnetic radiation will propagate during the time required for one oscillation.
Weight -- The gravitational force exerted on an object of a certain mass. The weight of mass m is mg Newtons, where g is the local acceleration due to a body's gravity.
WWW -- World-Wide Web.
X
X-band -- A range of microwave radio frequencies in the neighborhood of 8 to 12 GHz.
X-ray -- Electromagnetic radiation in the neighborhood of 100 picometer wavelength.
Z
Z -- Zulu in phonetic alphabet, stands for UT, Universal Time.
Zenith -- The point on the celestial sphere directly above the observer. Opposite the nadir.