
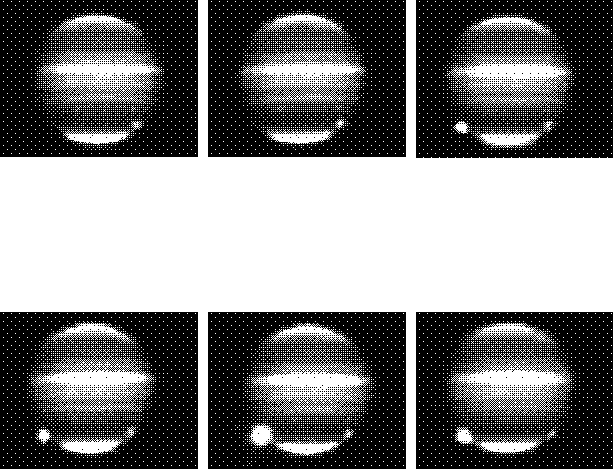
David Crisp, Vikki Meadows, Stuart Lumsden, Jonathan Pogson, and Steven Lee
The InfraRed Imaging Spectrometer (IRIS) is being used on the 3.9 m Anglo-Australian Telescope (AAT) at Siding Spring Observatory (near Coonabarabran, Australia) to monitor the impacts of the fragments of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 with Jupiter. On 18 July, observations of Jupiter were initiated at 6:30 UT, about one hour before sunset. The skies were clear, and the seeing was better than 1 arc-second. Near-infrared images and spectra at wavelengths between 2 and 2.4 microns taken between 6:30 and 7:30 UT on 18 July 1994 revealed two bright features near the evening terminator at about 45 South latitude. These features were identified as the impact sites of fragments A and C, which had been monitored on the previous day. Bright flashes associated with the impacts of fragments G2 and G1 were first detected on the morning limb of Jupiter at 7:33 and 7:40 UT, respectively. The impact flashes were tens to hundreds of times brighter than those seen previously. These sites were monitored until 13:30 UT.