Capturing Callisto
| Credit | NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Southwest Research Institute |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
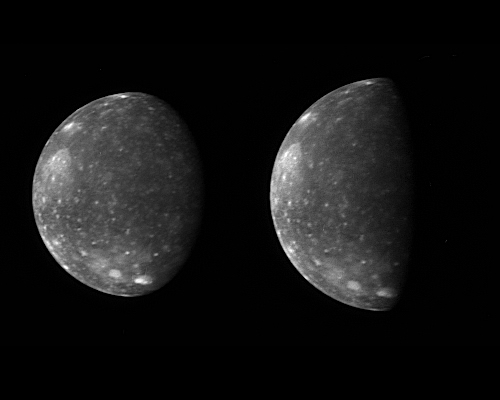
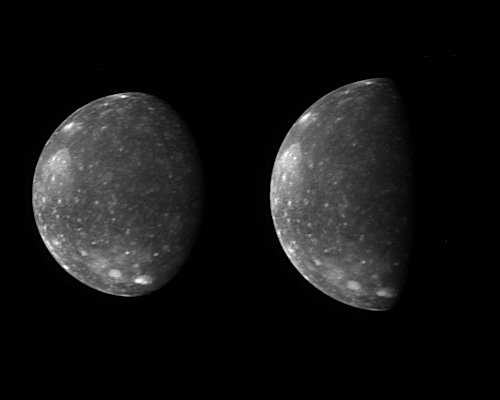
The New Horizons Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) captured these two images of Jupiter's outermost large moon, Callisto, as the spacecraft flew past Jupiter in late February 2007. New Horizons' closest approach distance to Jupiter was 2.3 million km (1.4 million miles), not far outside Callisto's orbit, which has a radius of 1.9 million km (1.2 million miles). However, Callisto happened to be on the opposite side of Jupiter during the spacecraft's pass through the Jupiter system, so these images, taken from 4.7 million and 4.2 million km (3.0 million and 2.6 million miles) away, are the closest obtained by New Horizons of Callisto.
Callisto's ancient, crater-scarred surface makes it very different from its three more active sibling satellites, Io, Europa and Ganymede. Callisto, 4,800 km (3000 miles) in diameter, displays no large-scale geological features other than impact craters, and every bright spot in these images is a crater. The largest impact feature on Callisto, the huge basin Valhalla, is visible as a bright patch at the 10 o'clock position. The craters are bright because they have excavated material relatively rich in water ice from beneath the dark, dusty material that coats most of the surface.
The two images show essentially the same side of Callisto -- the side that faces Jupiter -- under different illumination conditions. The images accompanied scans of Callisto's infrared spectrum with New Horizons' Linear Etalon Imaging Spectral Array (LEISA). The New Horizons science team designed these scans to study how the infrared spectrum of Callisto's water ice changes as lighting and viewing conditions change, and as the ice cools through Callisto's late afternoon. The infrared spectrum of water ice depends slightly on its temperature.
The left image, taken at 05:03 Universal Time on 27 February 2007, is centered at 5 degrees south, 5 degrees west, and has a solar phase angle of 46 degrees. The right image was taken at 03:25 Universal Time on 28 February 2007. It is centered at 4 degrees south, 356 degrees west and has a solar phase angle of 76 degrees.