Titan: Kraken and Ligeia In Sharper Focus
| Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute |
|---|---|
| PIA Number | PIA21434 |
| Language |
|
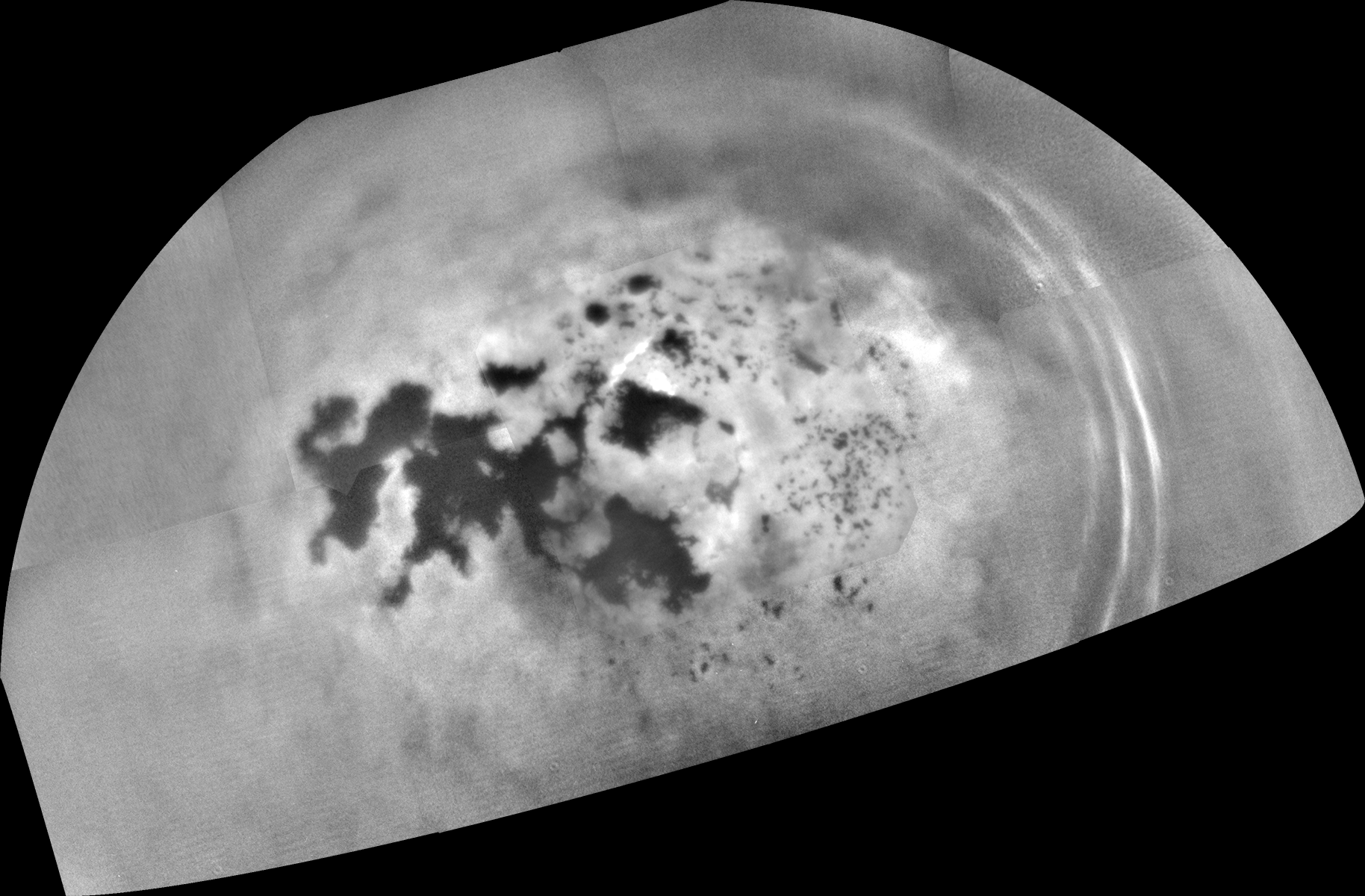
As it sped away from a relatively distant encounter with Titan on Feb. 17, 2017, NASA's Cassini spacecraft captured this mosaic view of the moon's northern lakes and seas.
Cassini's viewing angle over Kraken Mare and Ligeia Mare was better during this flyby than previous encounters, providing increased contrast for viewing these seas. Because the spacecraft is peering through less of Titan's haze toward Kraken and Ligeia, more details on their shorelines are visible, compared to earlier maps (see PIA19657).
This was one of several "non-targeted" Cassini Titan flybys in 2017 that allow the mission to image the moon's north polar region and track clouds there. ("Non-targeted" means Cassini did not have to use any rocket-thruster firings to steer itself toward the flyby.)
Several prominent cloud streaks are visible at mid-latitudes between 45 and 55 degrees north latitude, on the right side of the image. Smaller bright clouds are seen just above the sea called Punga Mare (roughly at center). Scientists are seeing increasing cloud activity in Titan's north polar region as the seasons continue to change from spring to summer there, though not as much as predicted by models of Titan's atmosphere.
The images in this mosaic were taken with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera using a spectral filter sensitive to wavelengths of near-infrared light centered at 938 nanometers.
The view was obtained at a distance of approximately 150,700 miles (242,500 kilometers) from Titan. Image scale is 1.6 miles (2.6 kilometers) per pixel. The view is an orthographic projection centered on 68 degrees north latitude, 225 degrees west longitude. An orthographic view is most like the view seen by a distant observer looking through a telescope.
The Cassini mission is a cooperative project of NASA, ESA (the European Space Agency) and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging operations center is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colorado.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov and http://www.nasa.gov/cassini. The Cassini imaging team homepage is at http://ciclops.org.
