News | January 27, 2010
Prometheus: Over Easy
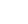
Looking for all intents and purposes like a celestial egg after a session in Saturn’s skillet, Prometheus displayed its pockmarked, irregular surface for NASA’s Cassini spacecraft on Jan. 27, 2010.
Prometheus is one of Saturn’s innermost moons. It orbits the gas-giant at a distance of 139,353 kilometers (85,590 miles) and is 86 kilometers (53 miles) across at its widest point. The porous, icy-bodied world was originally discovered by images taken by Voyager 1 back in 1980. You could say this latest “egg-cellent” view has the Cassini science team licking their chops at the thought of future Prometheus images.
This raw, unprocessed image of Prometheus [pro-MEE-thee-us] , taken in visible light, was obtained by Cassini’s narrow-angle camera at a distance of approximately 36,000 kilometers (23,000 miles).
The Cassini Equinox Mission is a joint United States and European endeavor. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Cassini orbiter was designed, developed and assembled at JPL.
For more information about the Cassini Equinox Mission visit: http://www.nasa.gov/cassini and http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov/.