3 min read
Cassini Significant Event Report
For Week Ending 07/03/98
Spacecraft Status:
The most recent Spacecraft status is from the DSN tracking pass on Monday, 06/29, over Madrid. The
Cassini spacecraft is in an excellent state of health and is executing the C8 sequence nominally. The speed of the spacecraft can be viewed on the "Where is Cassini Now?" web page (http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov/operations/present-position.cfm)
Inertial attitude control is being maintained using the spacecraft's hydrazine thrusters (RCS system). The
spacecraft continues to fly in a High Gain Antenna-to-Sun attitude. It will maintain the HGA-to-Sun attitude,
except for planned trajectory correction maneuvers, for the first 14 months of flight.
Communication with Earth during early cruise is via one of the spacecraft's two low-gain antennas; the antenna
selected depends on the relative geometry of the Sun, Earth and the spacecraft. The downlink telemetry rate is
presently 40 bps.
Spacecraft Activity Summary:
On Monday, 06/29, the quarterly Periodic Engineering Maintenance was performed as planned on board the
spacecraft. This activity consists of 3 parts: the Reaction Wheel Assembly (RWA) exercise, the Engine
Gimbal Actuator (EGA) exercise, and the AACS BAIL Maintenance.
The AACS RWA exercise spins the four Cassini reaction wheels for several minutes each for the purpose of
assuring that lubricants remain evenly distributed in the RWA mechanisms. The EGA exercise moves both
Cassini main engines through their range of motion to assure that gimbal lubricant remains evenly distributed.
The AACS BAIL software is stored on EEPROMs for the purpose of providing basic AACS capabilities for
use in the recovery from a deep undervoltage anomaly, should one ever occur. The BAIL maintenance is
performed to identify and repair any Single Bit Errors (SBEs) that may have occurred on the EEPROMs in
the preceding period. The activity will also identify, but not repair, any Double Bit Errors (DBEs); DBEs
would then be repaired by further commanding from the flight team at a later time.
On Wednesday, 07/01, the Solid State Recorder (SSR) record and playback pointers were reset, according
to plan. This housekeeping activity, done approximately weekly, maximizes the amount of time that recorded
engineering data is available for playback to the ground should an anomaly occur on the spacecraft.
Upcoming events:
Activities scheduled for the week of 07/03 - 07/09 include: SSR Pointer Reset (07/08), and uplink of the C9
Sequence (07/09). The C9 sequence is scheduled to begin on Sunday afternoon, July 12.
Additional information about Cassini-Huygens is online at http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov.
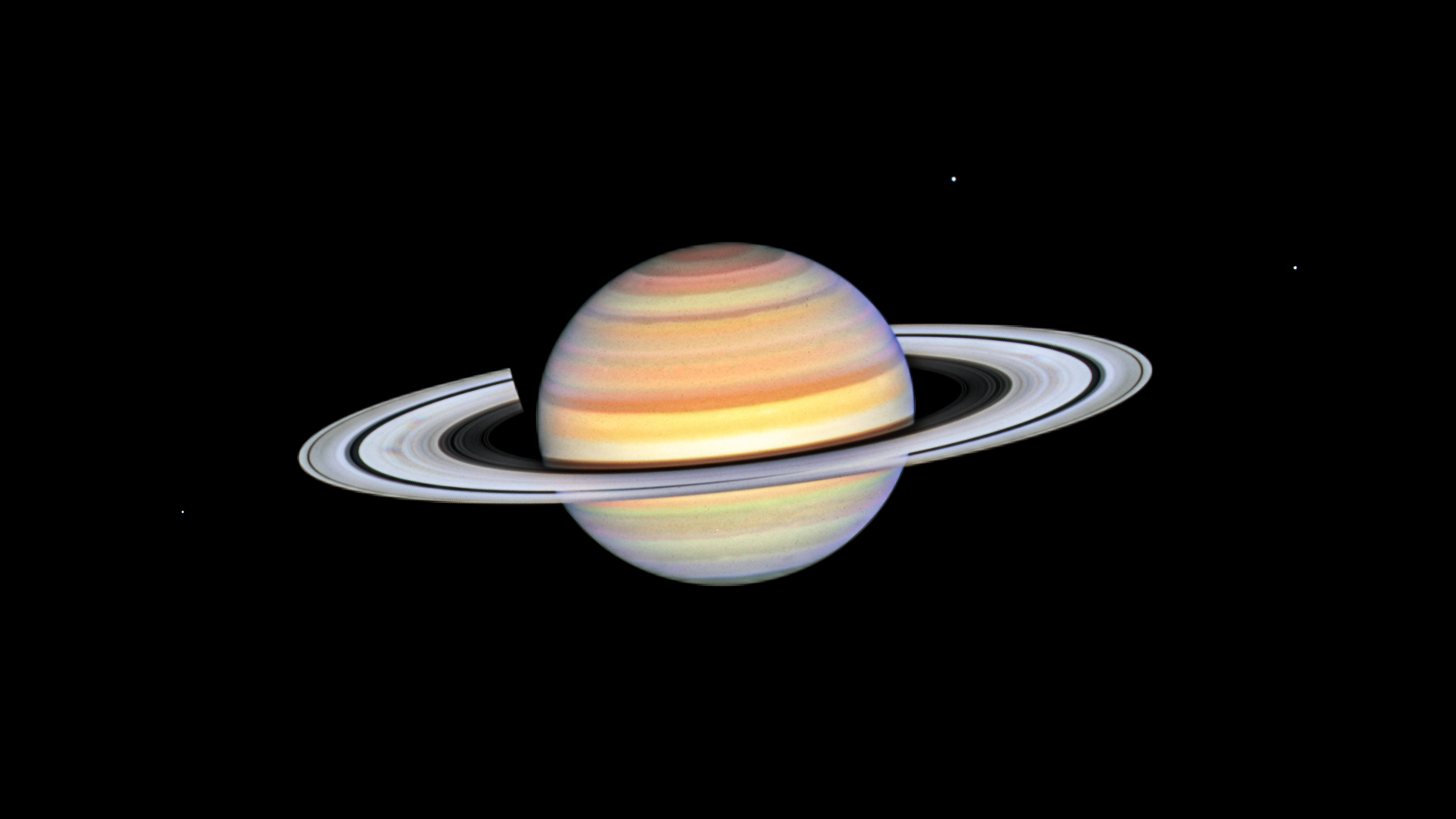
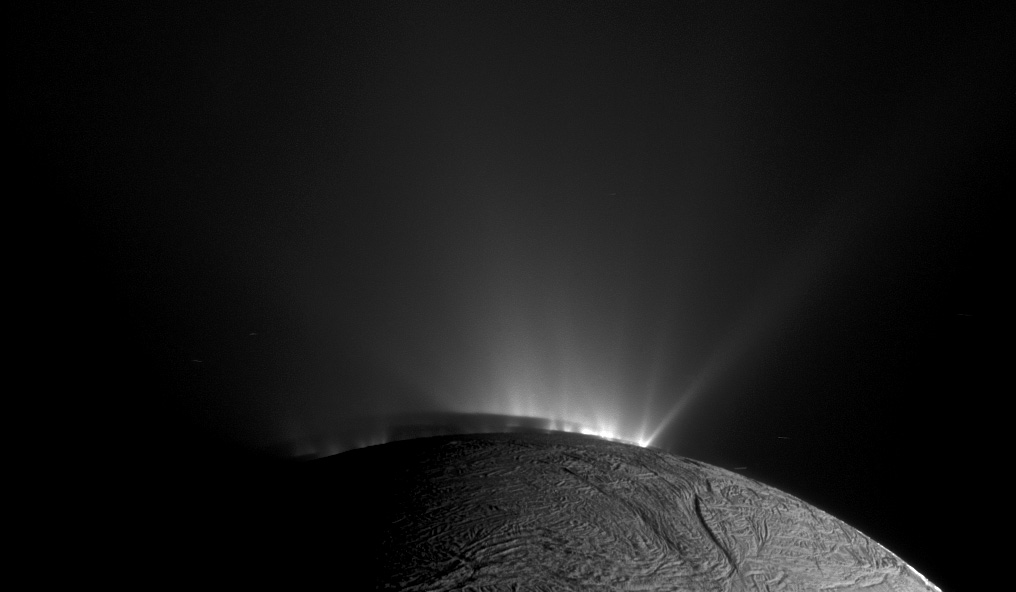
Cassini will begin orbiting Saturn on July 1, 2004, and release its piggybacked Huygens probe about six months later for descent through the thick atmosphere of the moon Titan. Cassini-Huygens is a cooperative mission of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Office of Space Science, Washington, D.C.
Media Relations Office
Jet Propulsion Laboratory
California Institute of
Technology
National Aeronautics and Space
Administration
Pasadena, Calif. 91109.
Telephone (818) 354-5011