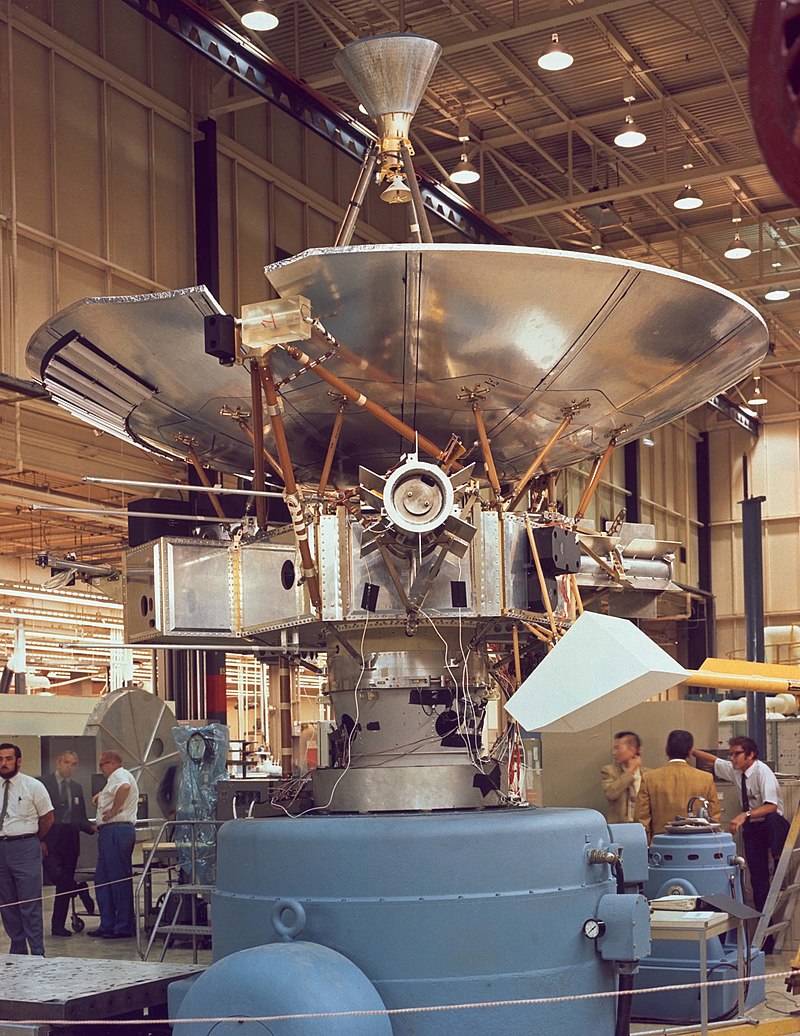
Able 5B (Pioneer P-31)
Able 5B (Pioneer P-31)
Type
Launch
Target
Objective
Like its two unsuccessful predecessors, this U.S. spacecraft was launched to orbit the Moon. Unfortunately, the Atlas Able booster malfunctioned and exploded a few seconds after launch.
What was Able 5B (Pioneer P-31)?
LIke its two unsuccessful predecessors, this U.S. spacecraft was launched to orbit the Moon. Unfortunately, the Atlas Able booster malfunctioned and exploded a few seconds after launch.
- The payload fell into the Atlantic Ocean about 7 to 12 miles (12 to 20 kilometers) from Cape Canaveral, Florida.
- This was the third and last attempt by NASA to launch a probe to orbit the Moon in the 1959–1960 period.
Nation | United States of America (USA) |
Objective(s) | Lunar Orbit |
Spacecraft | Pioneer P-31 / Able 5B |
Spacecraft Mass | 388 pounds (176 kilograms) |
Mission Design and Management | NASA / U.S. Air Force Ballistic Missile Division |
Launch Vehicle | Atlas Able (Atlas Able no. 3 / Atlas D no. 91) |
Launch Date and Time | Dec. 15, 1960 / 09:11 UT |
Launch Site | Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. / Launch Complex 12 |
Scientific Instruments |
|
Key Dates
Dec. 15, 1960: Launch
Dec. 15, 1960: Spacecraft destroyed seconds after launch
In Depth: Able 5B (Pioneer P-31)
The mission of Able 5B, like its two unsuccessful predecessors, was to orbit the Moon.
Scientific objectives included studying radiation near the Moon, recording the incidence of micrometeoroids, and detecting a lunar magnetic field.
Planned lunar orbital parameters, to be achieved about 60 hours after launch, were 2,700 × 1,500 miles (4,300 × 2,400 kilometers) with an orbital period of 9 to 10 hours.
The spacecraft had a slightly different scientific instrument complement than its predecessors, including a plasma probe experiment designed by NASA’s Ames Research Center that was to provide data on the energy and momentum distribution of streams of protons with energies above a few kilovolts per particle in the vicinity of the Moon.
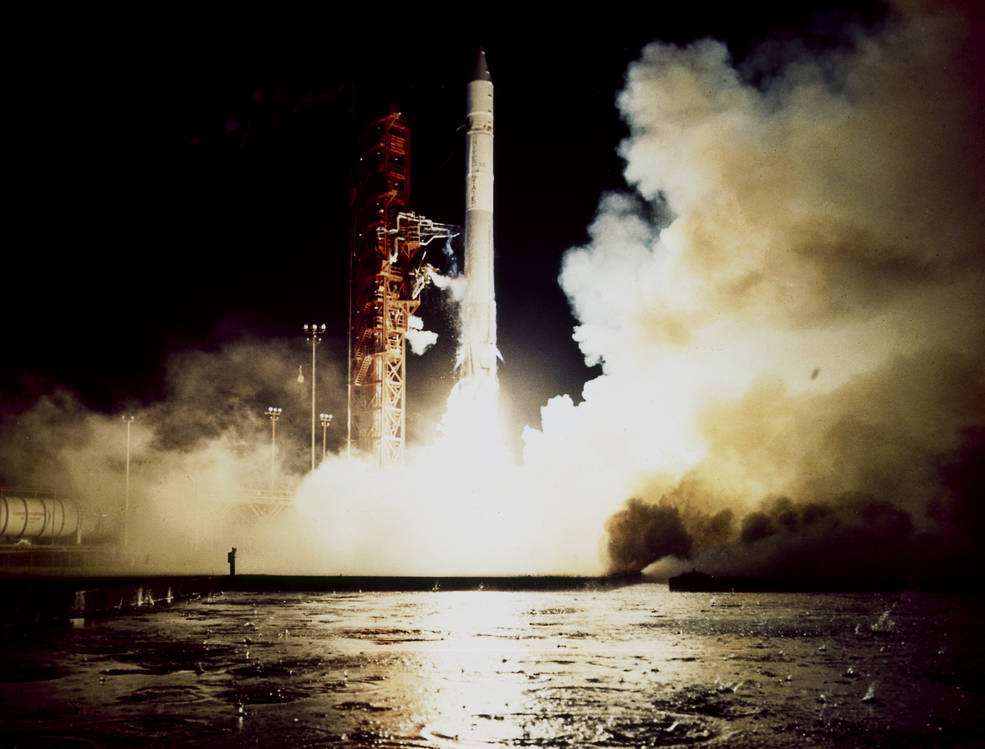
Unfortunately, the Atlas Able booster suffered a malfunction 66.68 seconds after launch and then exploded at T+74 seconds at an altitude of about 7.5 miles (12.2 kilometers).
An investigation indicated that the Able upper stage prematurely ignited while the first stage was still firing.
This was the third and last attempt by NASA to launch a probe to orbit the Moon in the 1959–1960 period.
Additional Resources
Key Source
Siddiqi, Asif A. Beyond Earth: A Chronicle of Deep Space Exploration, 1958-2016. NASA History Program Office, 2018.