Mars Express
NASA Participation
In partnership with their European colleagues, U.S. scientists are participating in the scientific instrument teams of the Mars Express mission. NASA's involvement with the mission includes joint development of a radar instrument called the Mars Advanced Radar for Subsurface and Ionospheric Sounding (MARSIS) with the Italian Space Agency.
The specific science objectives for MARSIS are to:
- Detect, map, and characterize subsurface material discontinuities in the upper crust of Mars, including liquid water-bearing zones, icy layers, and other geologic units and structures
- Characterize and map the elevation, roughness, and electromagnetic properties of the surface
- Probe the ionosphere of Mars to characterize the interaction of the atmosphere and the solar wind.
To date, MARSIS has already provided information about features beneath the Martian surface, including buried impact craters, layered deposits, and hints of deep underground water ice.
NASA's involvement also includes coordination of radio relay systems to make sure that different spacecraft operate together; a hardware contribution to the energetic neutral atoms analyzer instrument; and backup tracking support from NASA's Deep Space Network during critical mission phases.
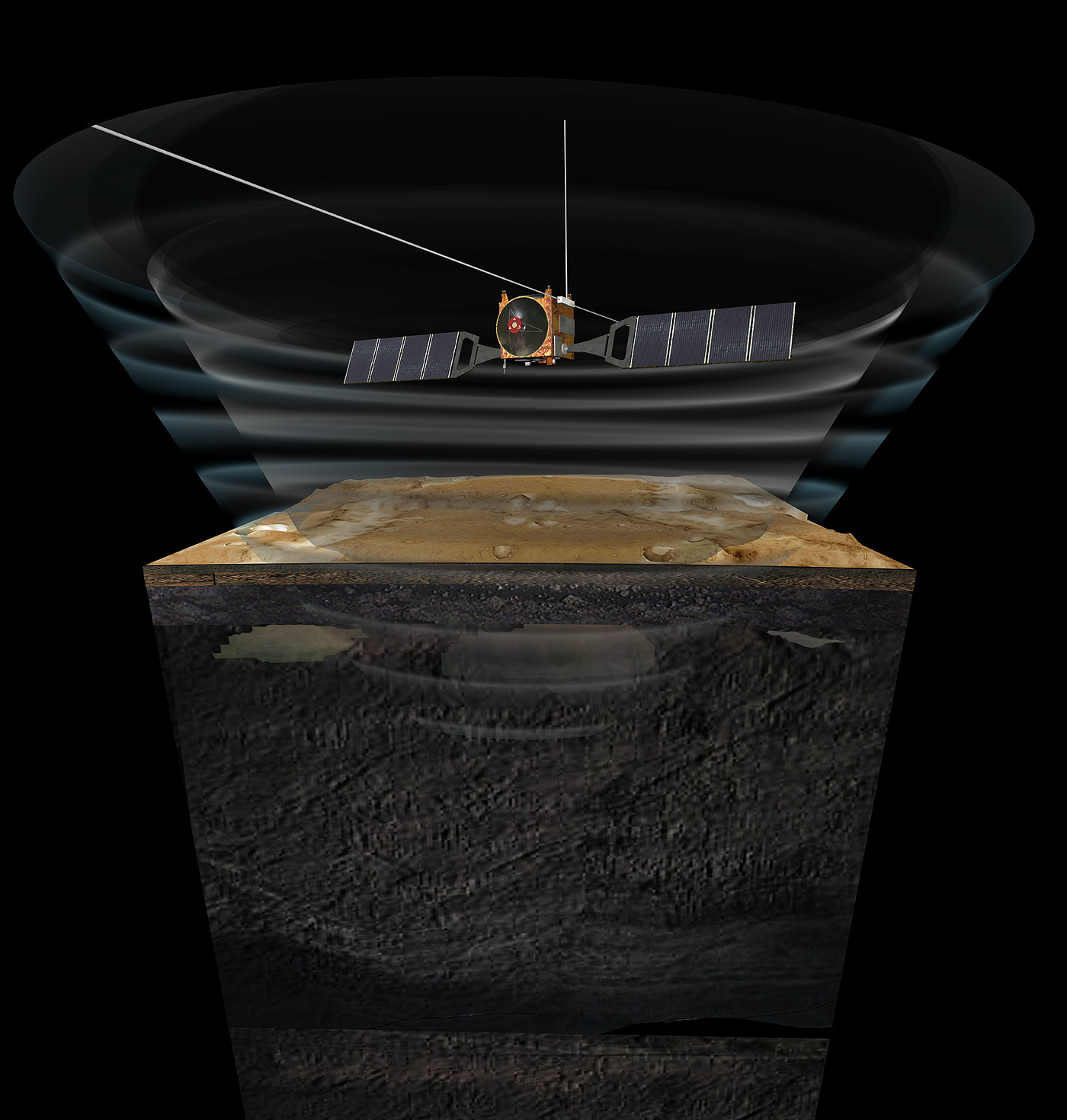
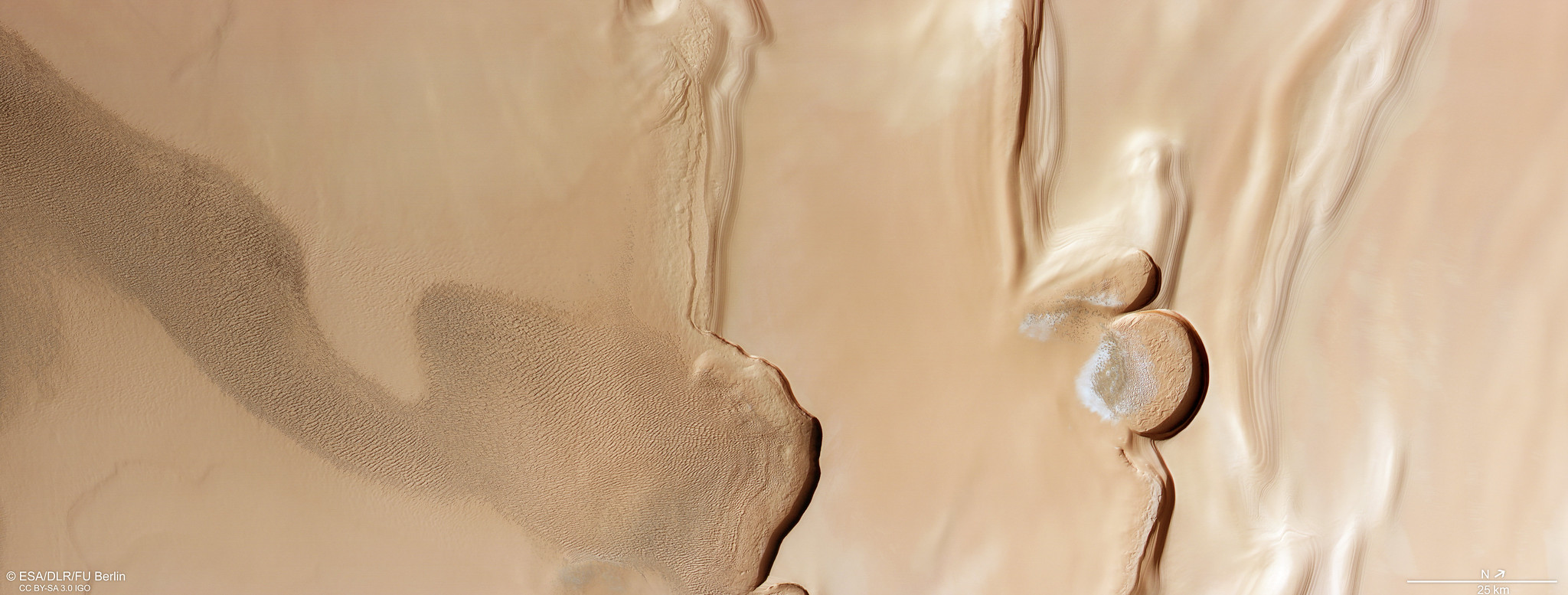
Two Radar Sounders Examine South Polar Layered Deposits on Mars
Two complementary radar sounder instruments work together to discover hidden Martian secrets. They are the MARSIS on ESA's Mars Express orbiter and the Shallow Subsurface Radar (SHARAD) on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
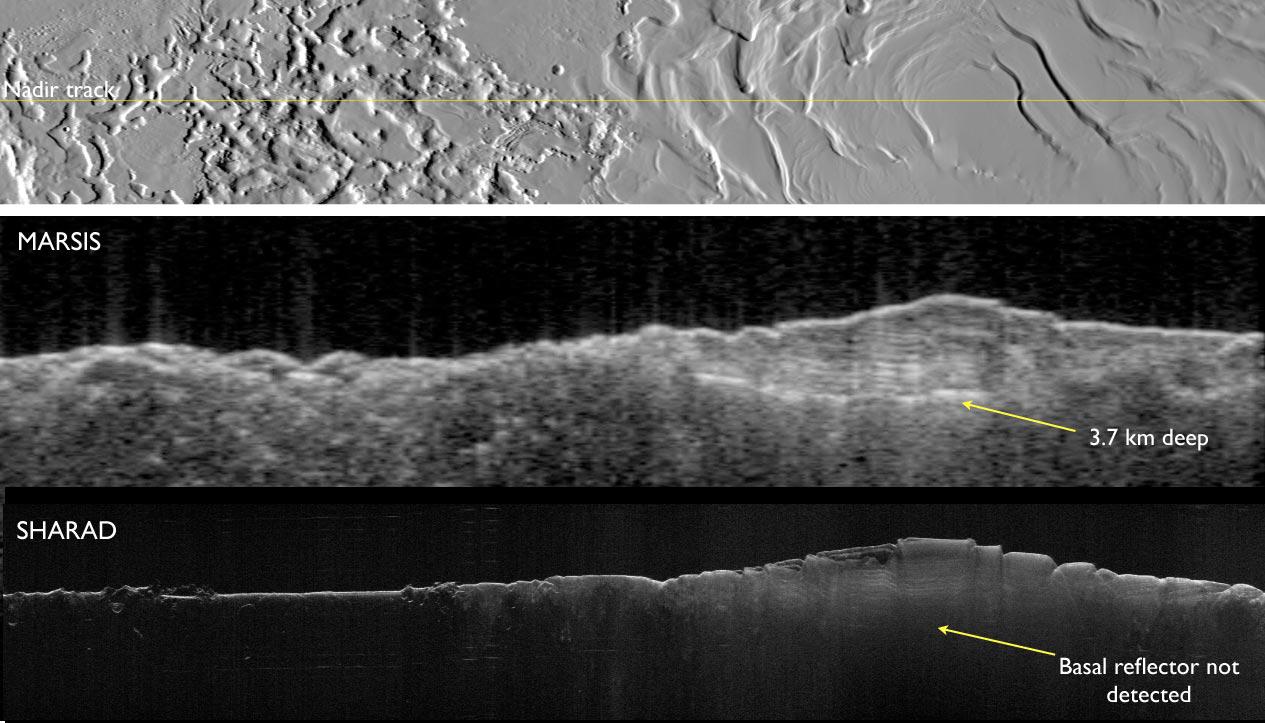
MARSIS was designed to penetrate deep and it has delivered on its promise. These images show the base of Mars' south polar layered deposits at the deepest recorded point of 2.3 miles (3.7 kilometers).
In contrast, SHARAD was designed as a high-resolution radar for a maximum penetration of 0.6 mile (1 kilometer), so it has difficulty detecting the base of these layered deposits.
MARSIS was funded by NASA and the Italian Space Agency and developed by the University of Rome, Italy, in partnership with NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. Italy provided the instrument's digital processing system and integrated the parts. The University of Iowa, Iowa City, built the transmitter for the instrument, JPL, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, built the receiver, and Astro Aerospace, Carpinteria, California, built the antenna. The ESA has more information about Mars Express at its mission website.
SHARAD was provided by the Italian Space Agency (ASI). Its operations are led by the University of Rome and its data are analyzed by a joint U.S.-Italian science team. JPL manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter for the NASA Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
Quick Facts
Launch: June 2, 2003 UTC
Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG/Fregat
Launch Location: Baikonur Cosmodrome, Russia
Orbit Insertion: Dec. 25, 2003
Mission Status: Still Operating

Science Goal
The overall science goal of the mission is to understand the possibilities for past or present life by conducting a thorough search for liquid water, which is necessary to life as we know it. While liquid water cannot last long on the surface of Mars, some water might be trapped underground where the increase in pressure and temperature could be sufficient to keep it liquid.
Science Objectives
The mission's main objective is to search for subsurface water from orbit. Seven scientific instruments on the orbiting spacecraft have conducted rigorous investigations to help answer fundamental questions about the geology, atmosphere, surface environment, history of water, and potential for life on Mars.
Objectives include:
- Global surveys of the topography of the Martian surface at 33-foot (10-meter) resolution
- Mineralogical mapping at 110-yard (100-meter) resolution
- Characterization of the subsurface to several yards, or kilometers, depth
- Analyses of atmospheric circulation, surface-atmospheric interactions, and interactions between the Martian atmosphere and the space environment