| |
The images below depict a series of images of the surface taken with both the “in-lens” secondary electron detector at increasing magnification. The “in-lens” detector is essentially a combination of the signals from backscattered electrons and surface electrons, showing contrast in which lighter areas correspond to heavier elements. The images taken at high magnification are somewhat fuzzy due to the fact that the electron beam was depositing a carbon film during imaging, a sign that the sample has hydrocarbon contamination at the surface. This is consistent with the hypothesis that there is “brown stain” on these samples. The progressively higher magnification images show increasing detail of what appears to be smears of material on the surface.
Genesis sample 60237, a fragment of diamond-like carbon on silicon (DOS), was analyzed using the SEM in a Zeiss CrossBeam Focused Ion Beam system without coating. |
| |
 |
|
Figure 1. Low magnification SEM montage image of Genesis sample 60237, imaged with the in-lens secondary electron detector, sensitive to conductivity changes in the surface among other properties. The arrow indicates an example of a SIMS pit. The black box shows the approximate location of the images in Figures 2.
+ Enlarge image |
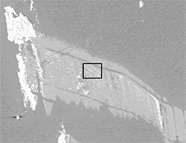 |
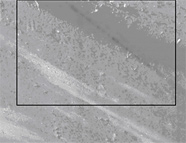
Figure 2. The feature outlined in Figure 1(sample 60237) imaged with the in-lens secondary electron detector. The outlined area is shown in detail in Figure 3.
+ Enlarge image
|
| |
 |
|
Figure 3. The area outlined in Figure 2 (sample 60237) imaged with the in-lens secondary electron detector. The outlined area is shown in detail in Figure 4.
+ Enlarge image |
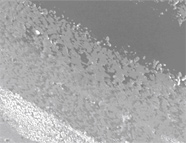 |
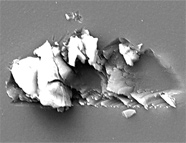
Figure 4. The area outlined in Figure 3 (sample 60237) imaged with the in-lens secondary electron detector.
+ Enlarge image |
| |
Genesis Sample 60300 |
| |
 |
|
Figure 5. An SEM image of an embedded particle in SiOS (sample 60300), which remained after cleaning using both hot Aqua-Regia and a cellulose acetate replica film. The particle appears to be sapphire from another wafer.
+ Enlarge image |
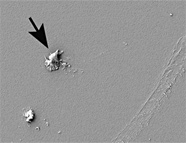 |
Figure 6. An SEM image of SiOS (sample 60300) showing several “smudges” of contamination. The arrow indicates a smudge of hydrocarbon contamination.
+ Enlarge image |
| |
Genesis Sample 60236 |
|
|
|
|
| |
 |
|
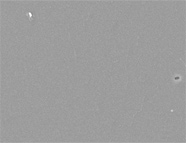
Figure 7. SEM image of Genesis sample 60236, imaged with secondary electron detector. Very slight topography is present.
+ Enlarge image |
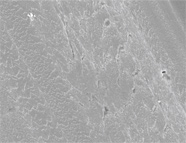 |
Figure 8. SEM image of Genesis sample 60236 in Figure 7, but imaged with the “in-lens” secondary detector. The lack of topography in Figure 7 seems to indicate that this is a very slight smudge of material on top of the sample rather than a scratch.
+ Enlarge image |
| |
 |
|
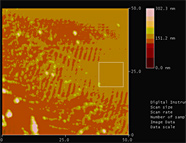
Figure 9. Large field of view AFM image of “smudge” in Figure 8. The parallel “ridges” at approximately 13° from vertical are artifacts. What looked like a “scratch” is actually raised material indicating a “smudge.”
+ Enlarge image |
|
|
| |
Genesis Sample 60122
Two extraction replicas were made of Genesis sample 60122 (this sample was not cleaned) using replicating tape (cellulose acetate). The replicas were coated with approx. 20 nm of evaporated carbon to create TEM samples once the cellulose acetate is dissolved away using acetone vapor. Before the TEM samples are created, we imaged the replicas and the original sample after the second replica using a high resolution SEM. Carbon coating is not ideal for SEM imaging and better images could be obtained with a gold/platinum coat. However, the imaging demonstrates the ability of the replicating tape to remove even 10 nm particles from the surface, which will allow them to be analyzed in a TEM for composition, morphology and crystallinity. |
| |
 |
|
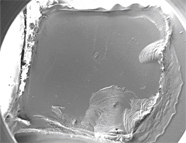
Figure 10. SEM images of the first extraction replica fabricated from sample 60122.
Top: View of entire carbon replica.
Bottom: Representative image of submicron particles embedded in the replica.
+ Enlarge image |
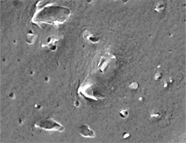 |
Figure 11 . SEM images of the first extraction replica fabricated from sample 60122. Top: View of entire carbon coated replica.
Bottom: Representative image of submicron particles embedded in the replica.
+ Enlarge image |
| |
|
|
|
|
