| Johnson Space
Center cleanroom Certified (07-99) |

View 11 minute educational video on
cleanroom technology.
 Teacher
Guide Teacher
Guide
 Student
Activity Student
Activity |
Teachers, use these instructional materials
to fully engage your students. Adobe Acrobat Reader
required (see below). |
To read print-optimized files, download Adobe
Acrobat Reader.
An important milestone for future outreach work was attained
in mid-July 1999. The Genesis spacecraft will carry a science
canister containing pure materials in which to collect solar
wind particles and return its valuable cargo to Earth for
analysis. The cleanroom where the science canister was assembled
at the Johnson Space Center (JSC) in Houston, Texas, was
certified in July as functioning at the high purity level
that it was designed for.
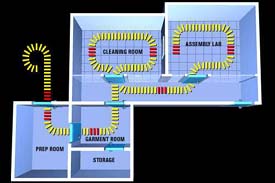 |
| Cleanroom
facility floor plan.
Courtesy: Johnson Space Center |
For the array assembly process and eventual archiving of
the returned solar wind samples, JSC built a cleanroom facility
dedicated to the Genesis mission. The new cleanroom was
designed and is supervised by Dr. Eileen Stansbery, contamination
control lead for the Genesis mission at JSC.
Stansbery states that the primary objective of this cleanroom
is to "protect [the Genesis spacecraft's] collector surfaces
from contamination before and after" they are exposed to
solar wind in space. "To do that implies a non-contaminated
installation and a clean payload interior." Additionally,
some payload components need to be cleaned individually
before they are installed in the canister.
Cleanrooms are used in hospitals, in the production of
electronic equipment, and for the curation of samples. Despite
the name, cleanrooms are never totally contaminant-free.
They are classified from a rating of 100,000 down to 1 by
the amount of contamination present during operation. Class
1 cleanrooms are the most sanitary. There can be no more
than one dust particle larger than 1 micron across per cubic
foot of air moving through it in one minute.
The average room in a house has approximately 350,000 dust
particles of that size moving through a cubic foot of air
in a minute; thus it is class 350,000. Hospital operating
rooms are typically class 10,000 to class 1,000. The JSC
cleanroom used for the Genesis assembly is certified as
class 10. Collector materials must be as pure as possible
when sent into space. In 2004, when the solar wind samples
are returned to Earth, scientists will know that any ions
embedded in the wafers are from the solar wind.
 |
Technician in "bunny
suit" examines collector wafer inside JSC cleanroom.
Courtesy: Johnson Space Center
|
Technicians enter the JSC cleanroom facility through a
dressing area where they don protective clothing called
"bunny suits." Rather than protecting the technicians from
their environment, these suits protect the cleanroom from
the technicians' bodies, including skin flakes and other
contaminants.
The cleanroom has floors containing many small holes.
Air is constantly moving down from the ceiling, sweeping
air-borne contaminants through the floor and into special
cleaner-traps to remove particulate contaminants. The cleaned
air moves up through the walls of the room to be reintroduced
through the ceiling.
 |
| Engineering
model of Genesis science canister.
Courtesy: Jet Propulsion Laboratory |
To test the cleanroom and procedures for working in it,
Stansbery's team recently completed a dress rehearsal for
the processing of the complete science canister using an
engineering model. This is a mock-up of the container for
the collector arrays and the concentrator, components that
will hold samples of solar wind until they are returned
to Earth in 2003. This particular engineering model has
been used to test other features of the Genesis spacecraft
as well.Don Sevilla, payload team leader from the Jet Propulsion
Laboratory (JPL), which directs the Genesis mission, was
at JSC to watch the canister disassembly and re-assembly
procedure.
Sevilla was most interested in the cleaning process, and
the process for verifying the cleanliness of the final product.
He commented on the "good team spirit" between staff from
JPL and JSC working together on the project. Staff members
at JSC were very impressed by the new cleanroom's purity,
and by how clean it remained during the mock procedure.
Stansbery is excited about the opportunity to participate
in the Genesis mission. "The public will own the [Genesis]
solar wind samples," she says. "In essence, they will be
a national resource."
