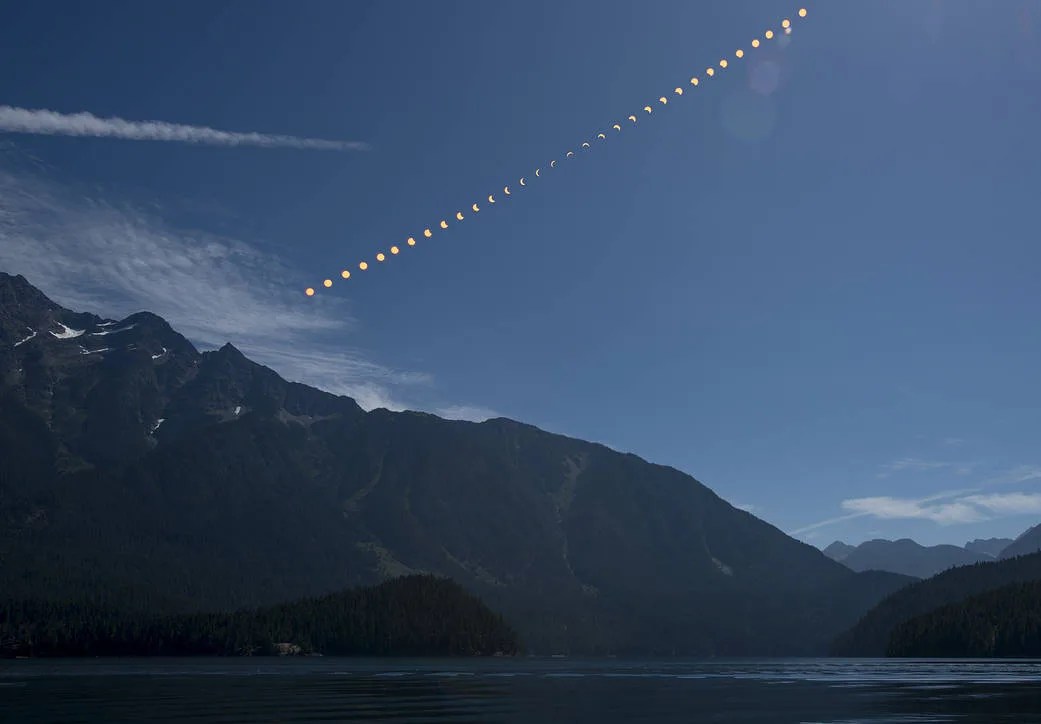
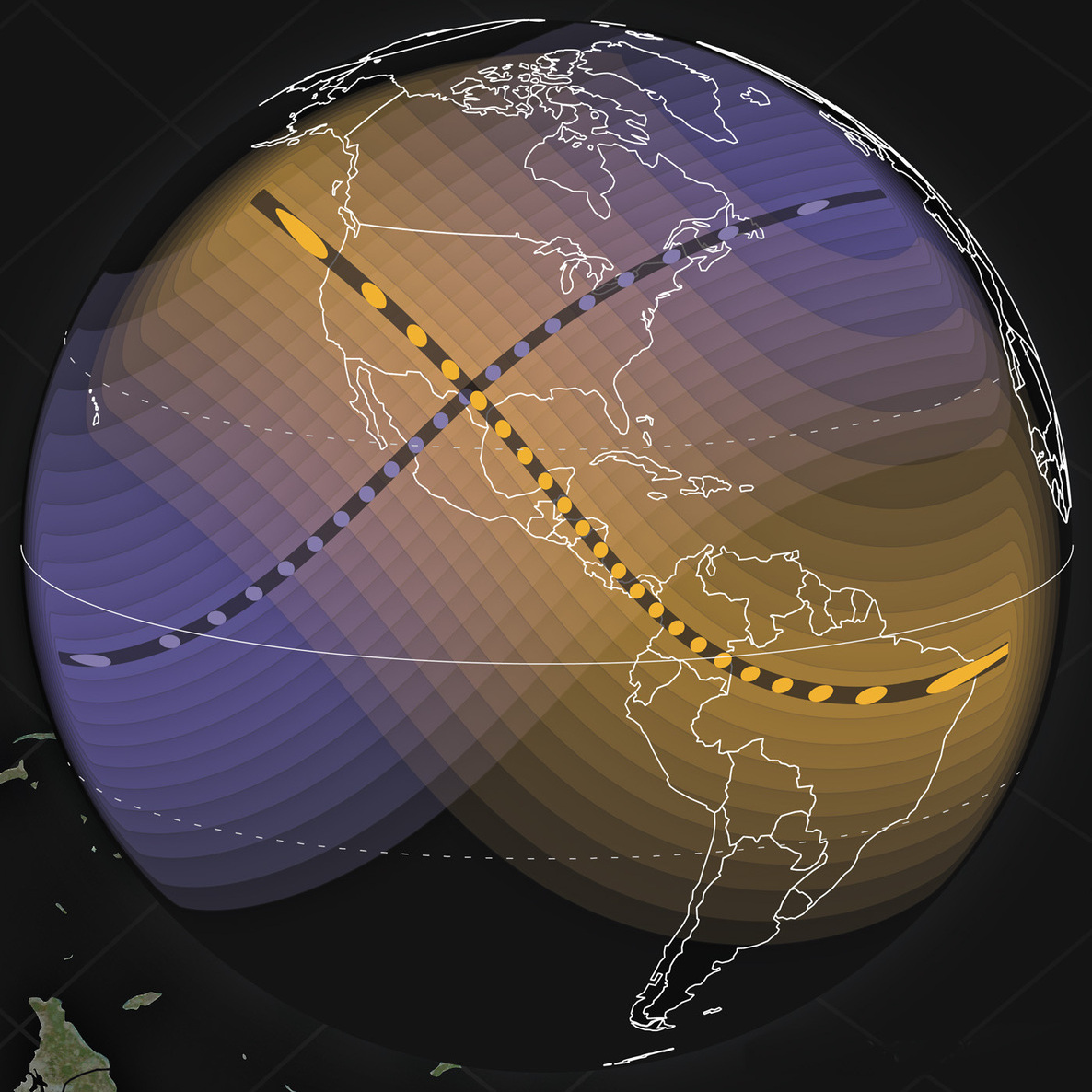
How the 2024 Total Solar Eclipse Is Different than the 2017 Eclipse
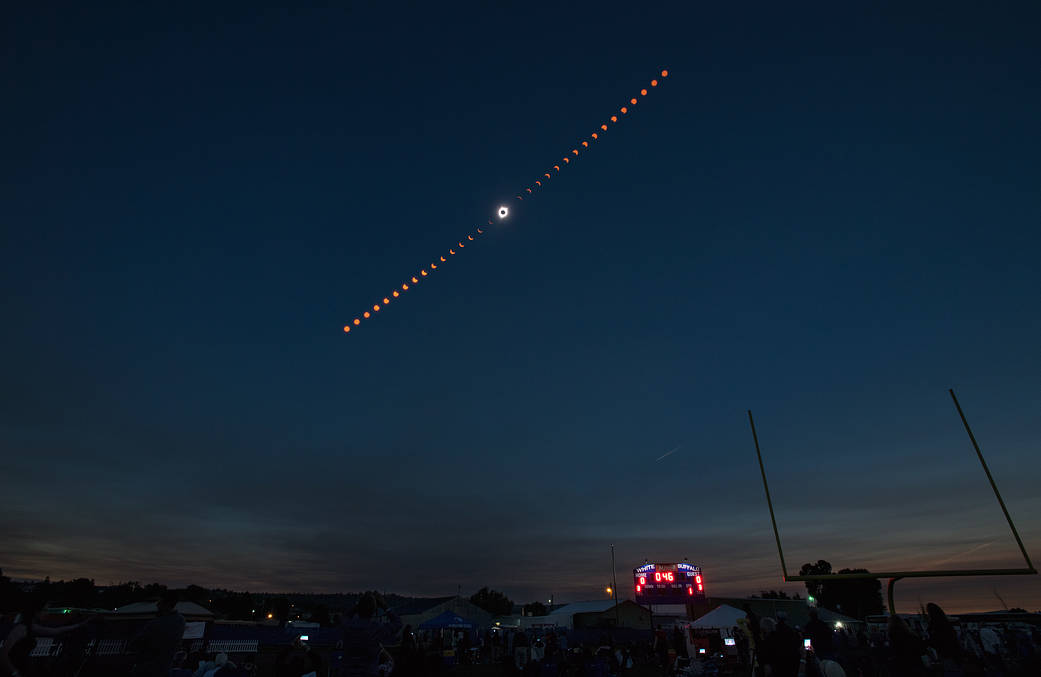
On April 8, the Moon’s shadow will sweep across the United States, as millions will view a total solar eclipse.…
Read the Story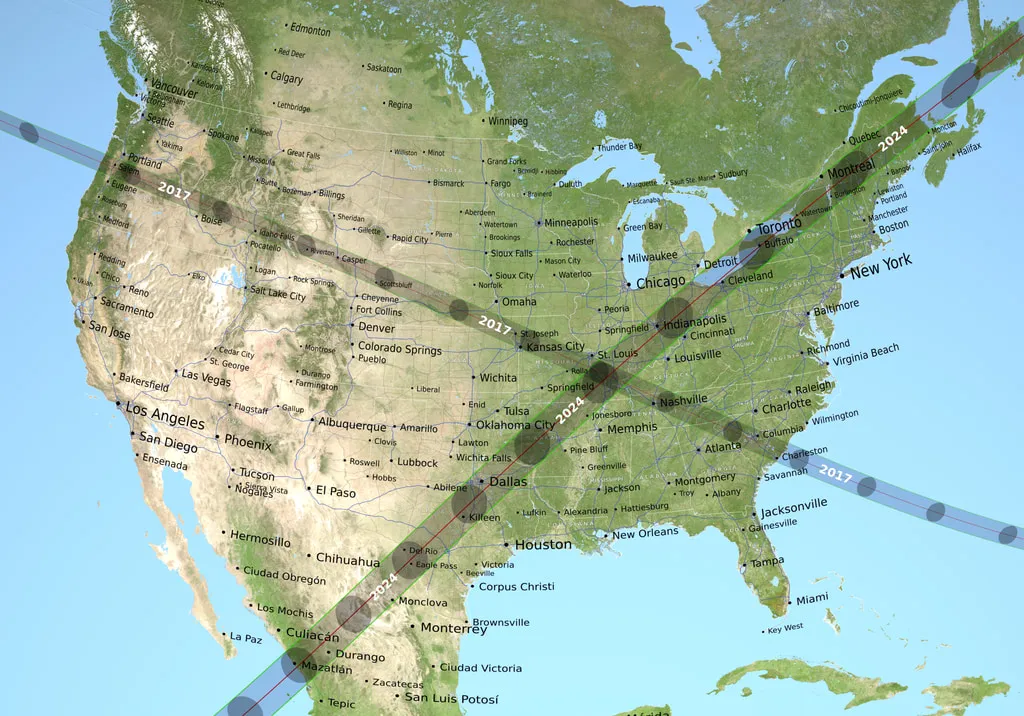
About Eclipses
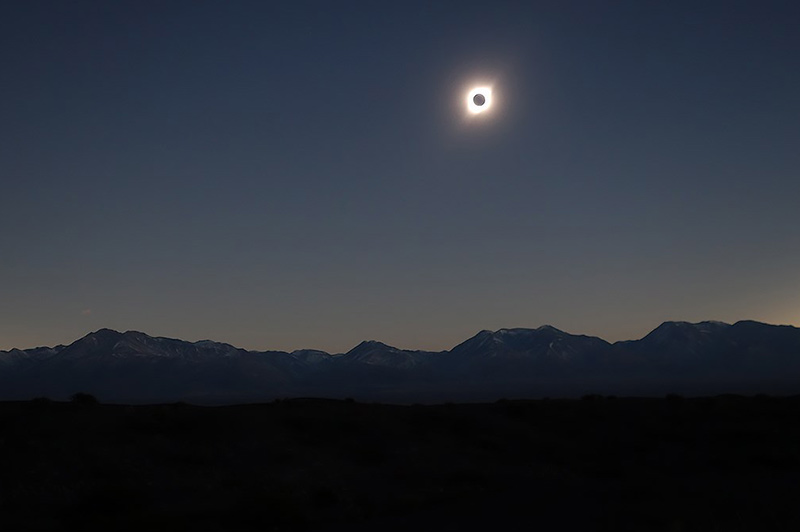
An eclipse is an awe-inspiring celestial event that drastically changes the appearance of the two biggest objects we see in our sky: our Sun and Moon. On Earth, people can experience solar and lunar eclipses when Earth, the Moon, and the Sun line up. Safety is the number one priority when viewing a solar eclipse. Be sure to follow these safety guidelines when viewing a solar eclipse.
Quick Facts
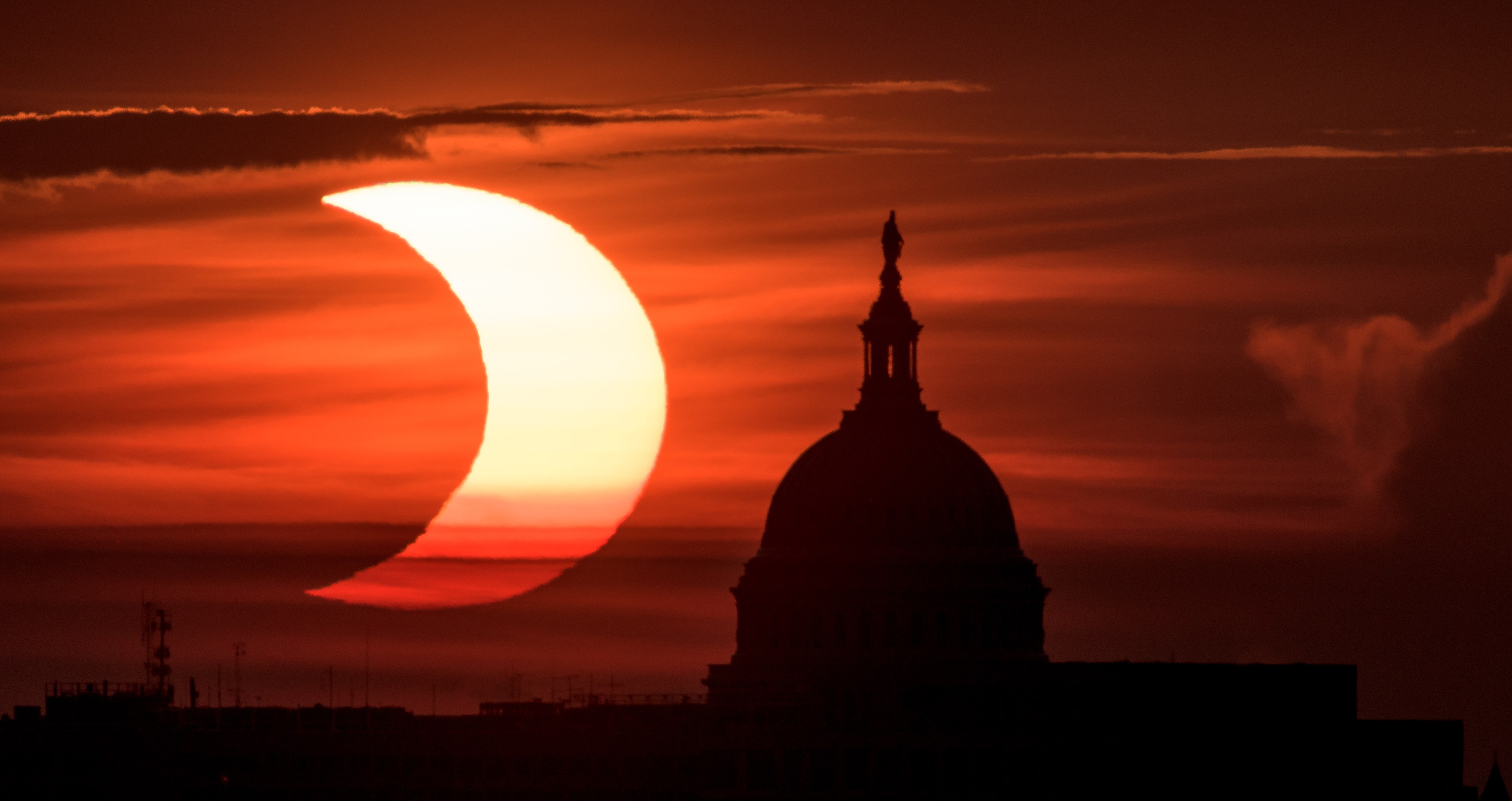

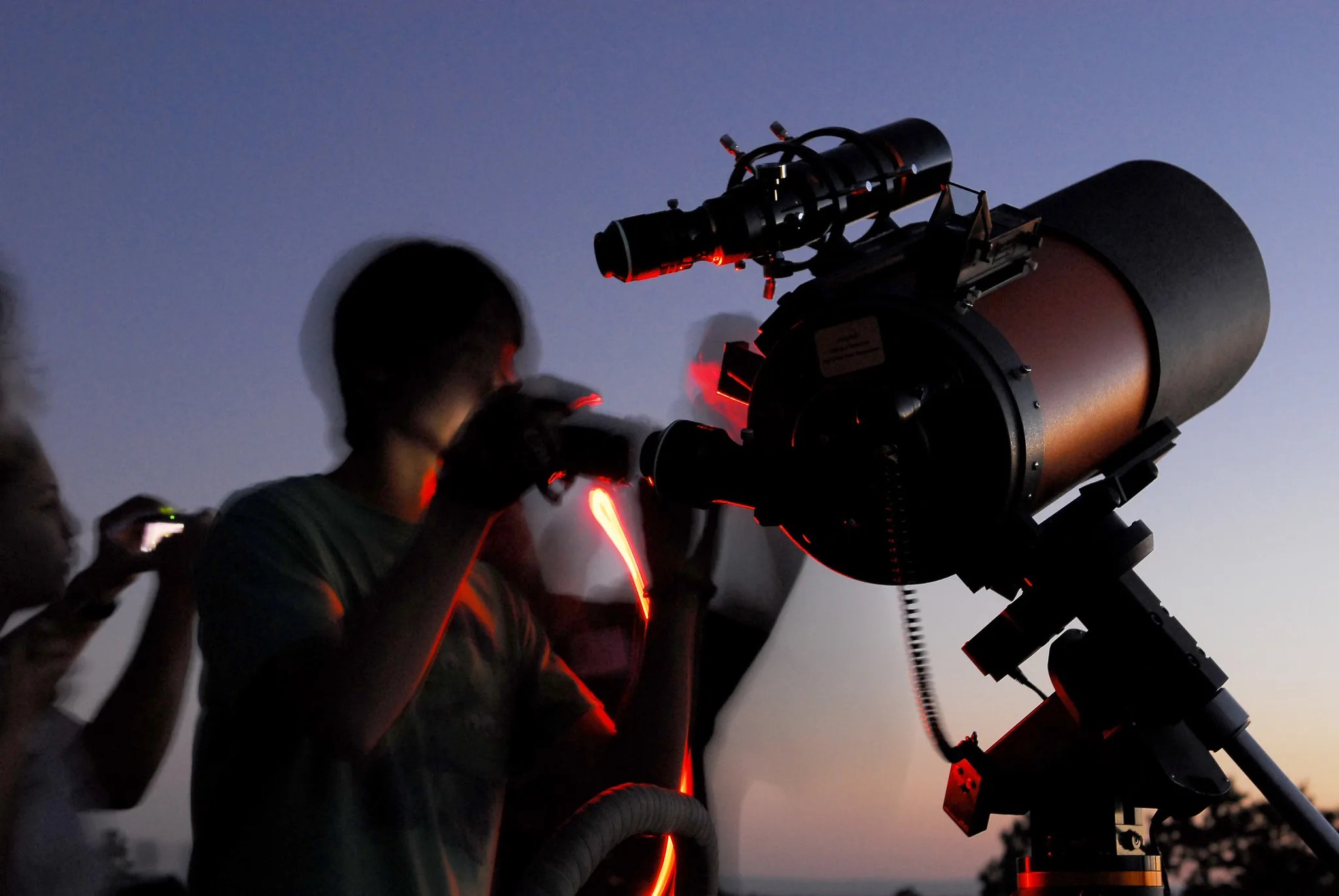
Eye Safety During an Eclipse
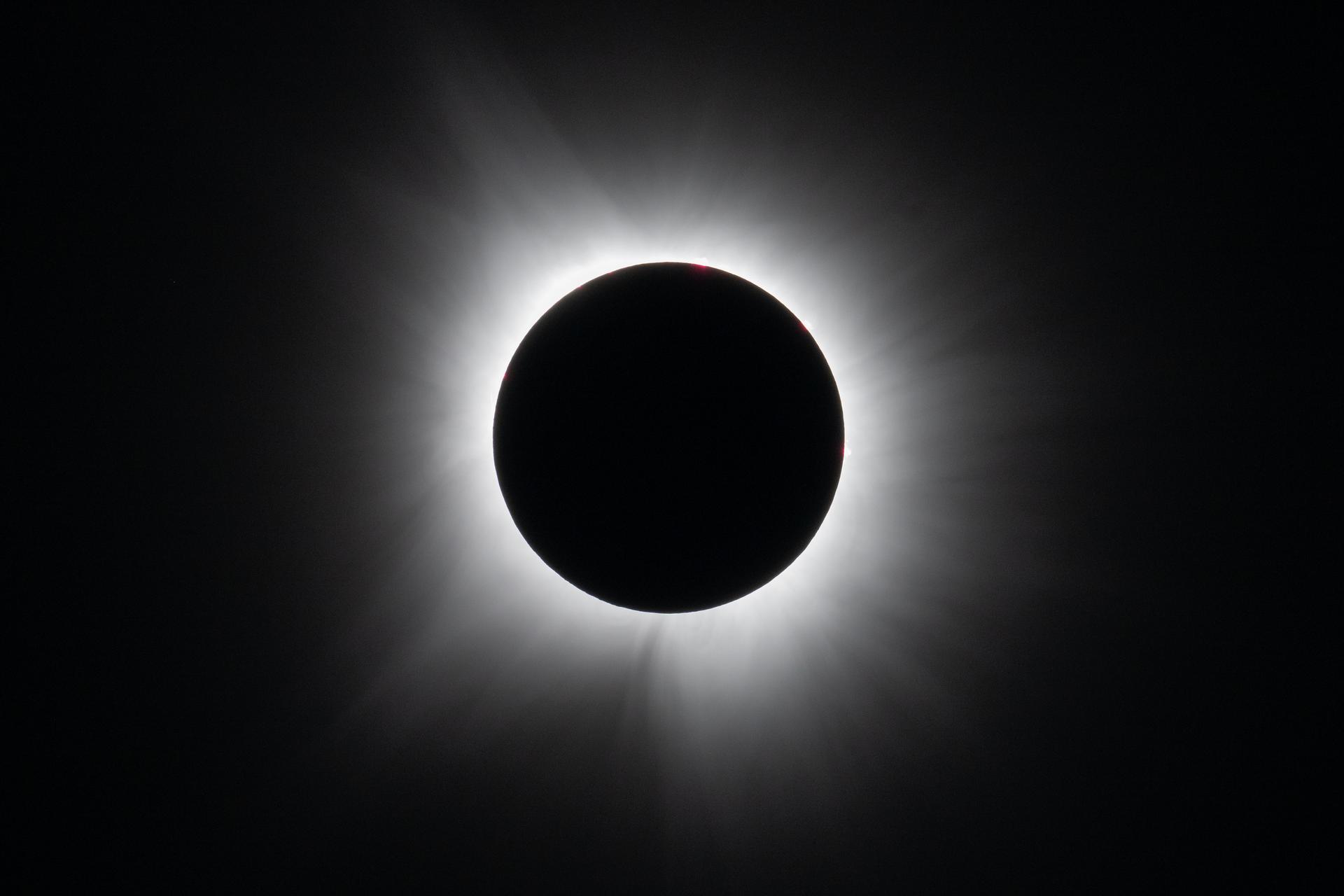
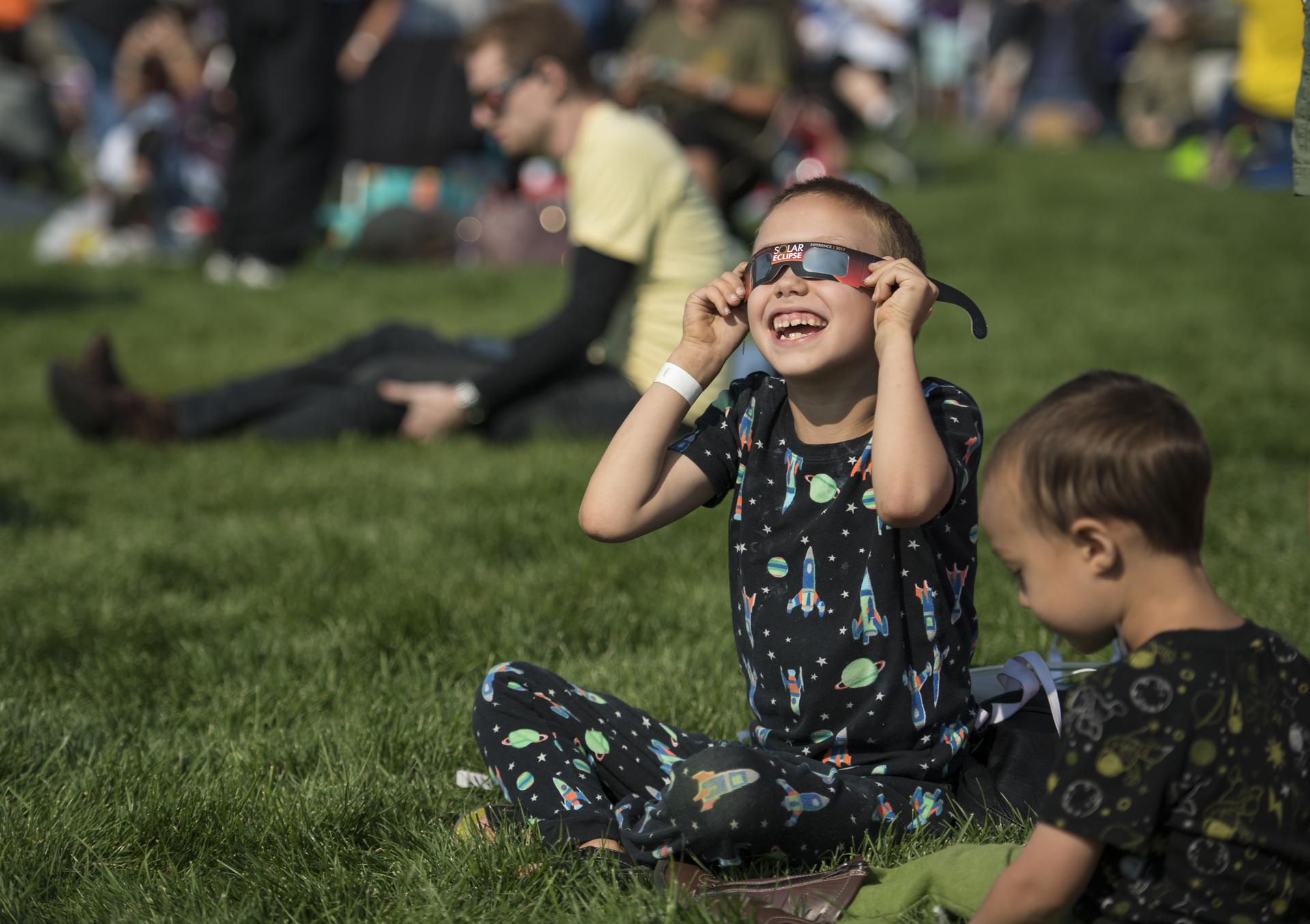
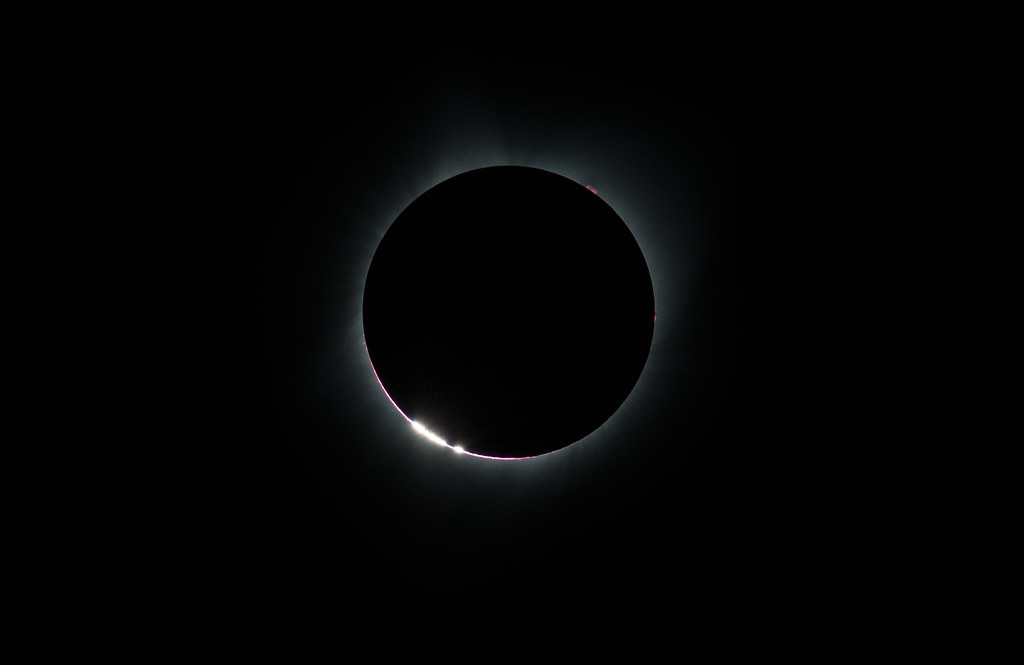
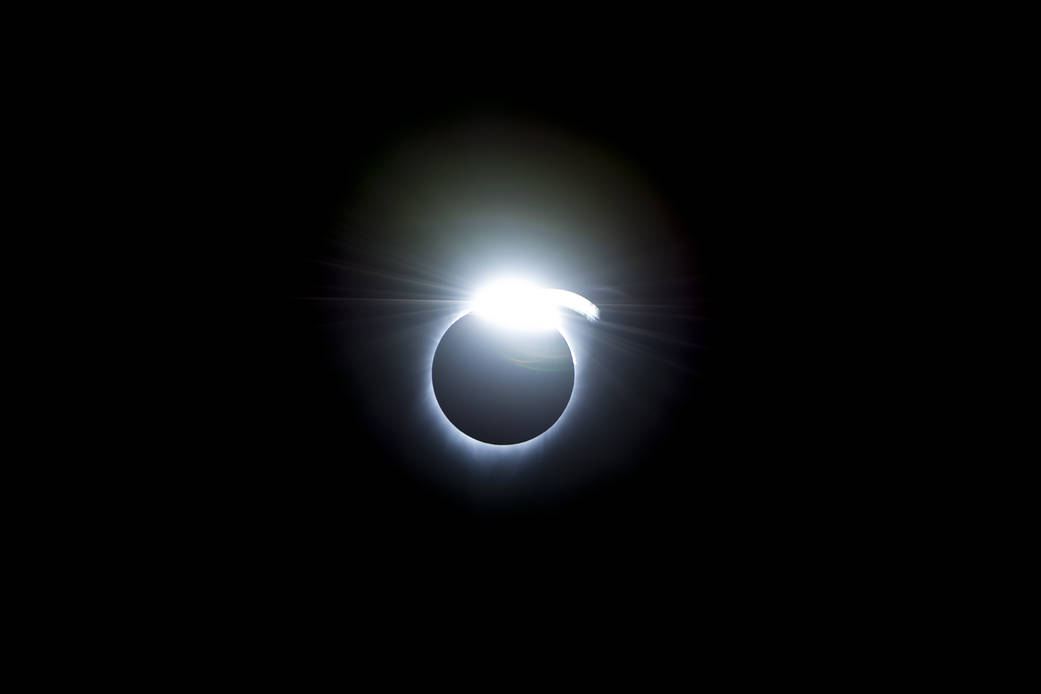
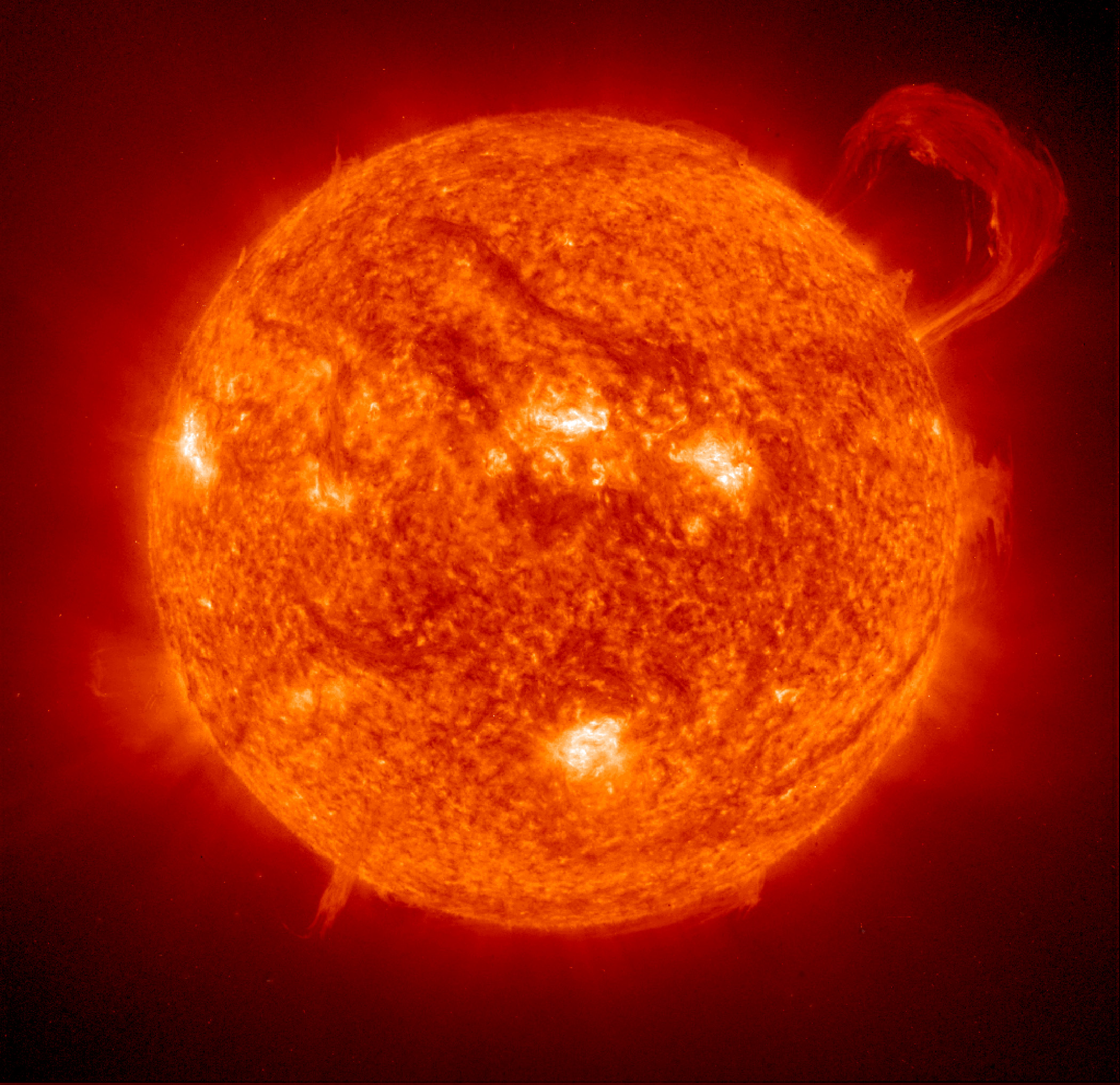
Observing our star, the Sun, can be safe and inspirational.
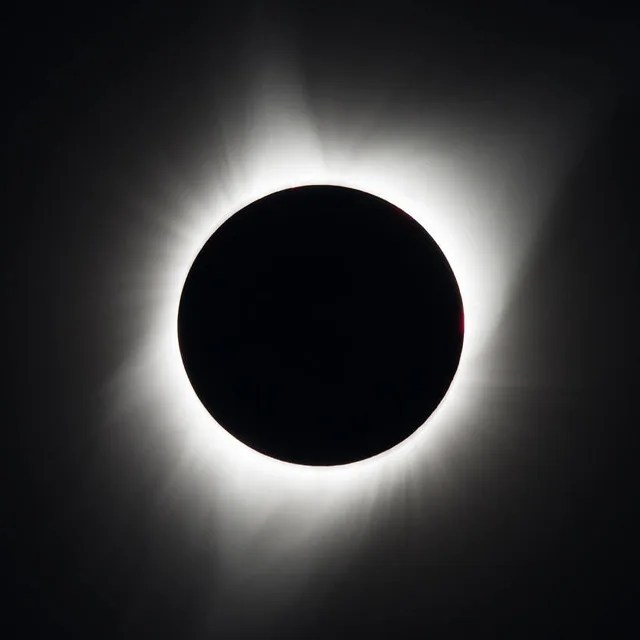
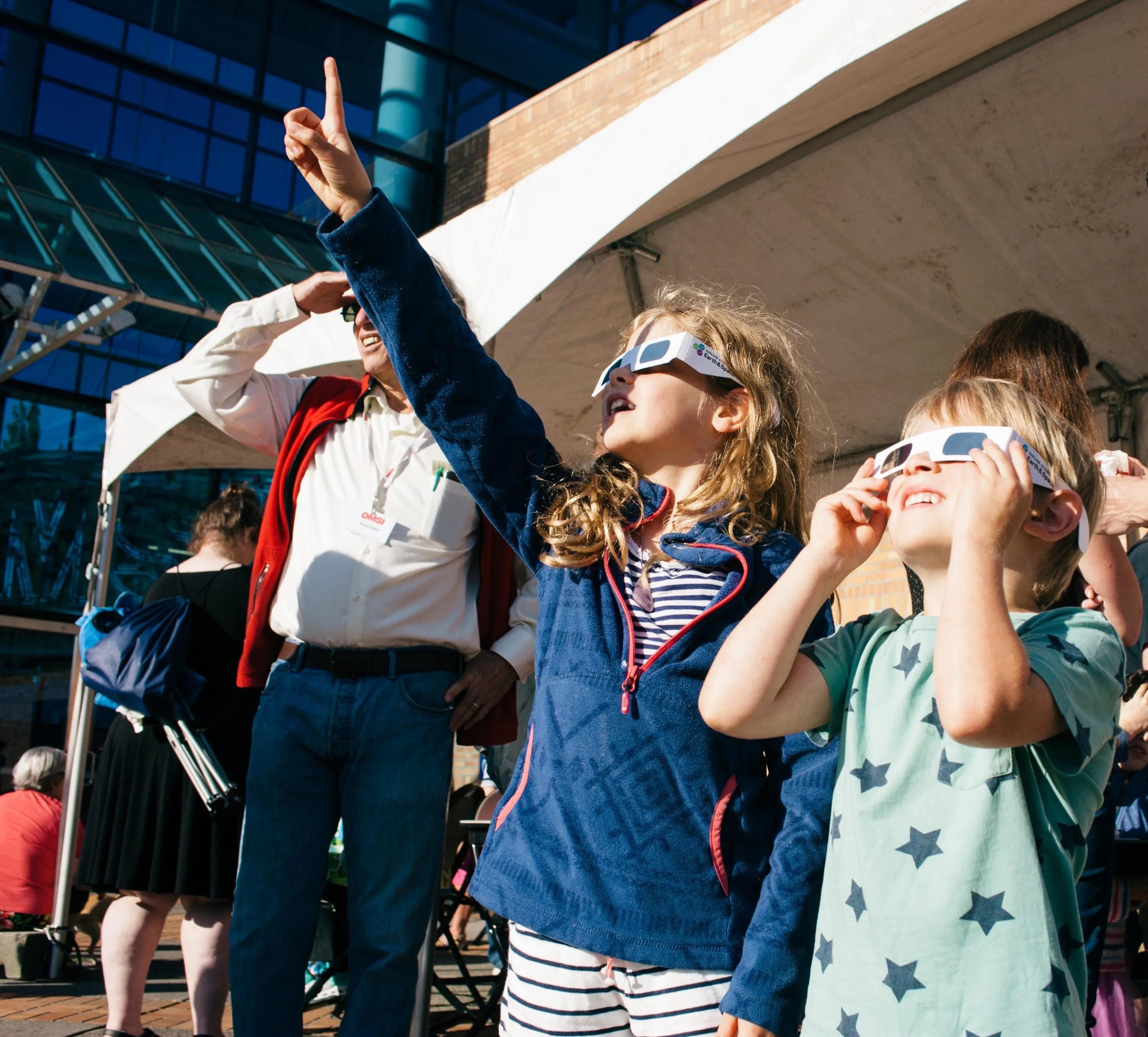
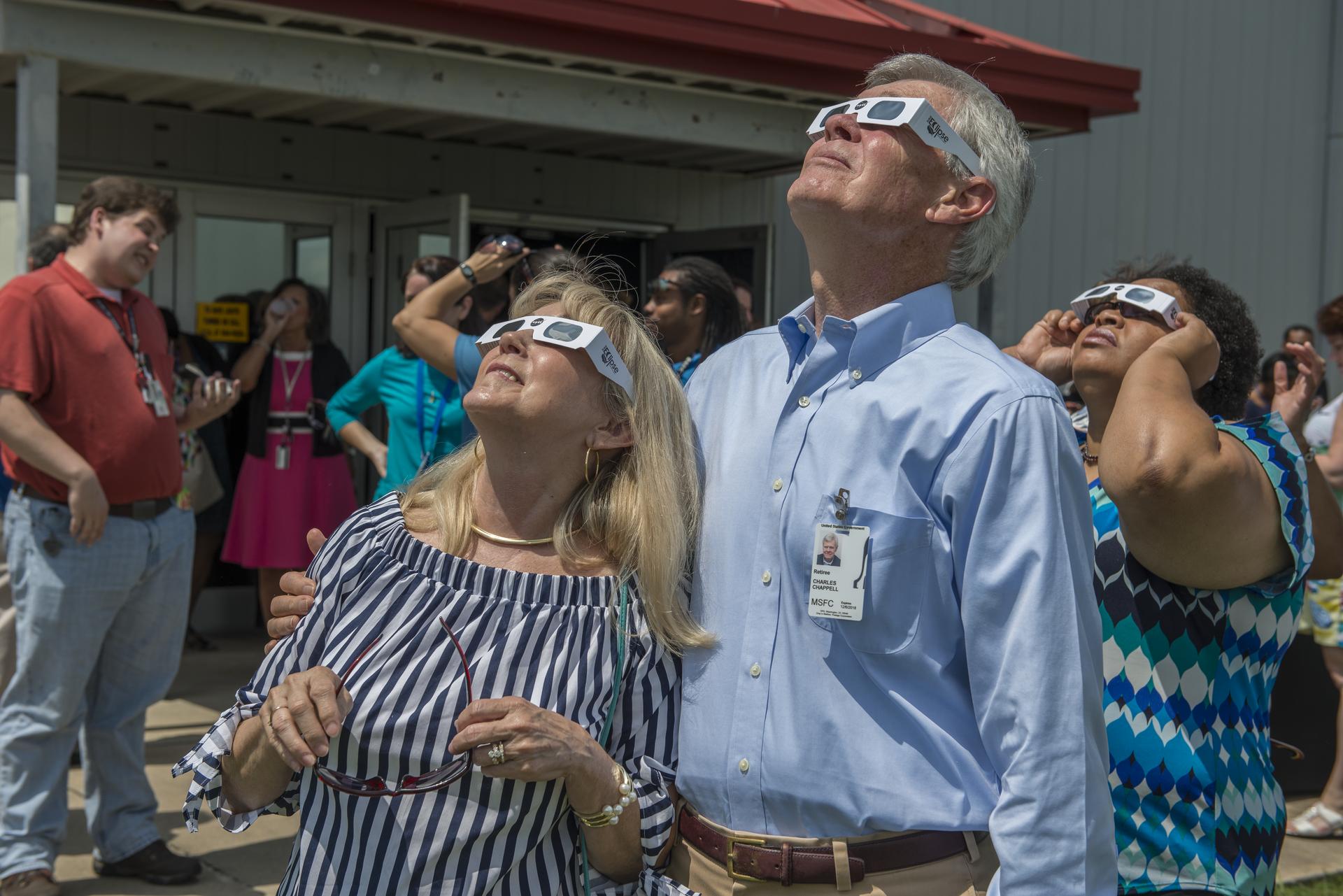
Except for a specific and brief period of time during a total solar eclipse, you must never look directly at the Sun without proper eye protection, such as safe solar viewing glasses (eclipse glasses). Eclipse glasses are NOT the same as regular sunglasses; regular sunglasses are not safe for viewing the Sun. During a total solar eclipse, you must wear your eclipse glasses (or use other solar filters) to view the Sun directly during the partial eclipse phase. You can only take your glasses off during the short time when the Moon completely obscures the Sun – known as the period of totality. If you don’t have eclipse glasses, you can use an indirect viewing method, such as a pinhole projector, which projects an image of the Sun onto a nearby surface.
It is safe to look at the Moon with unprotected eyes or through a telescope during all types and during all stages of a lunar eclipse.

Citizen Science Projects
Observing a solar eclipse is one of many ways to get in on the fun of doing science.
You can get involved with NASA science by participating in a number of NASA-funded citizen science projects. Citizen science projects are collaborations between scientists and interested members of the public. Through these collaborations, volunteers (known as citizen scientists) have helped make thousands of important scientific discoveries.
Read More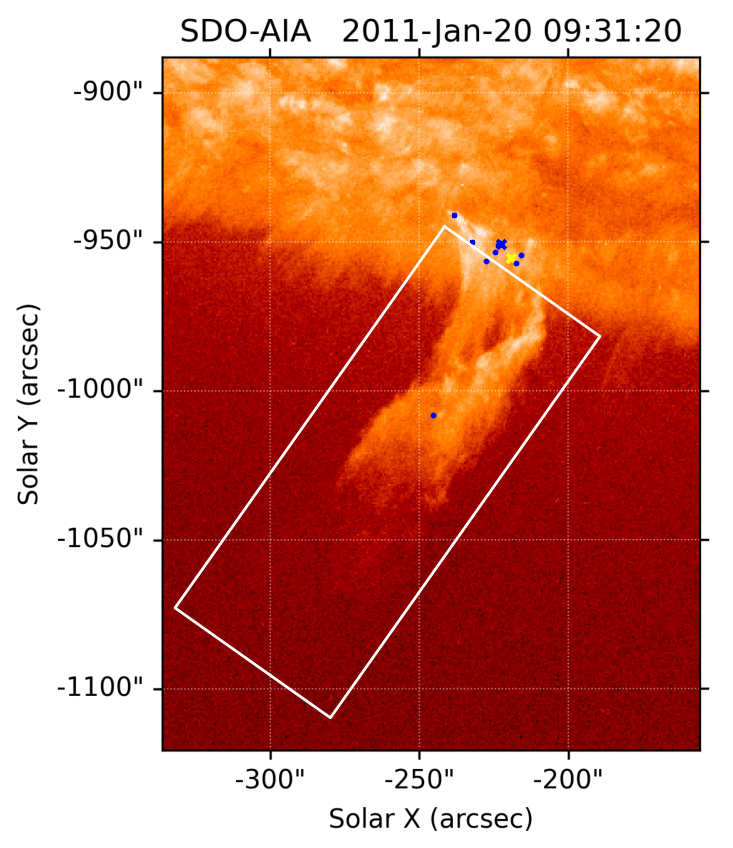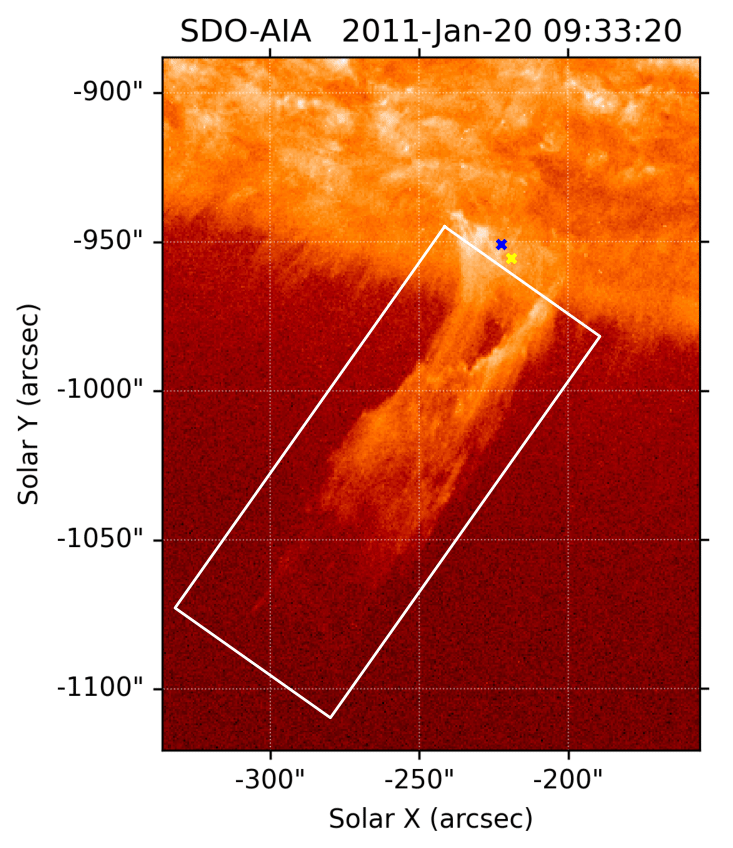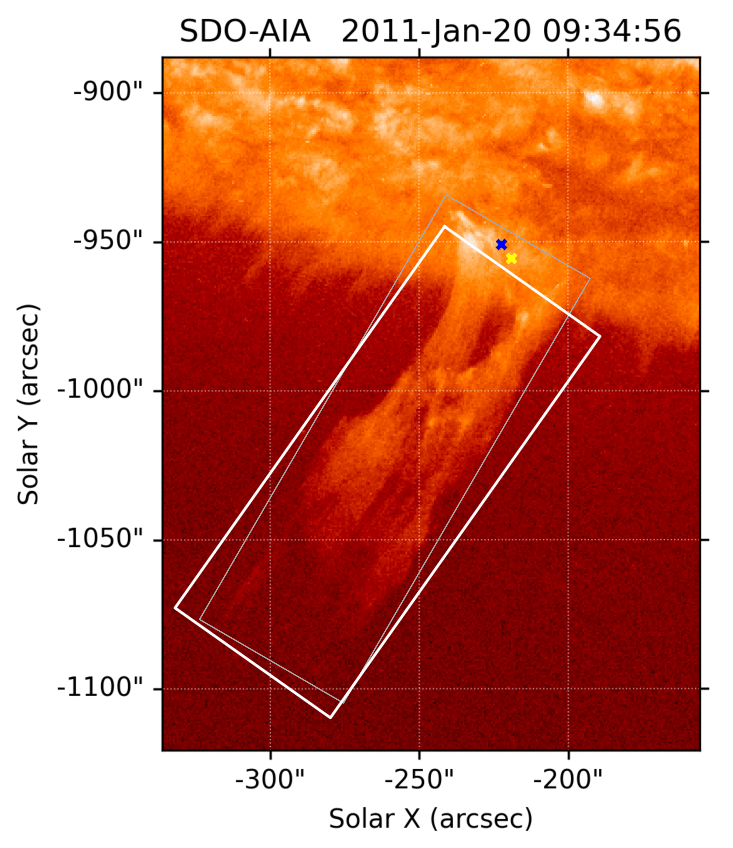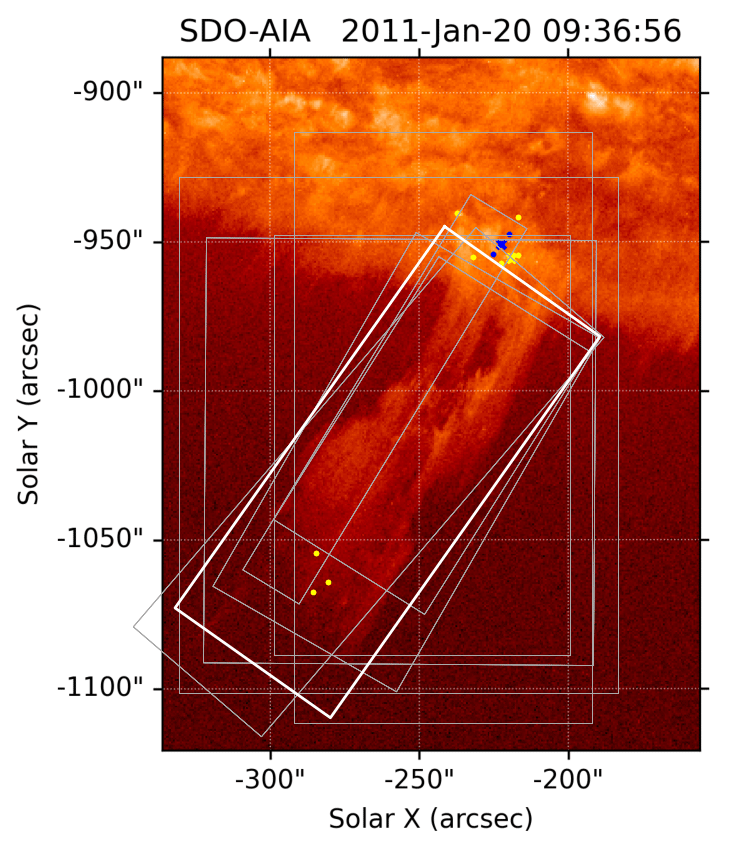
Know your eclipses!
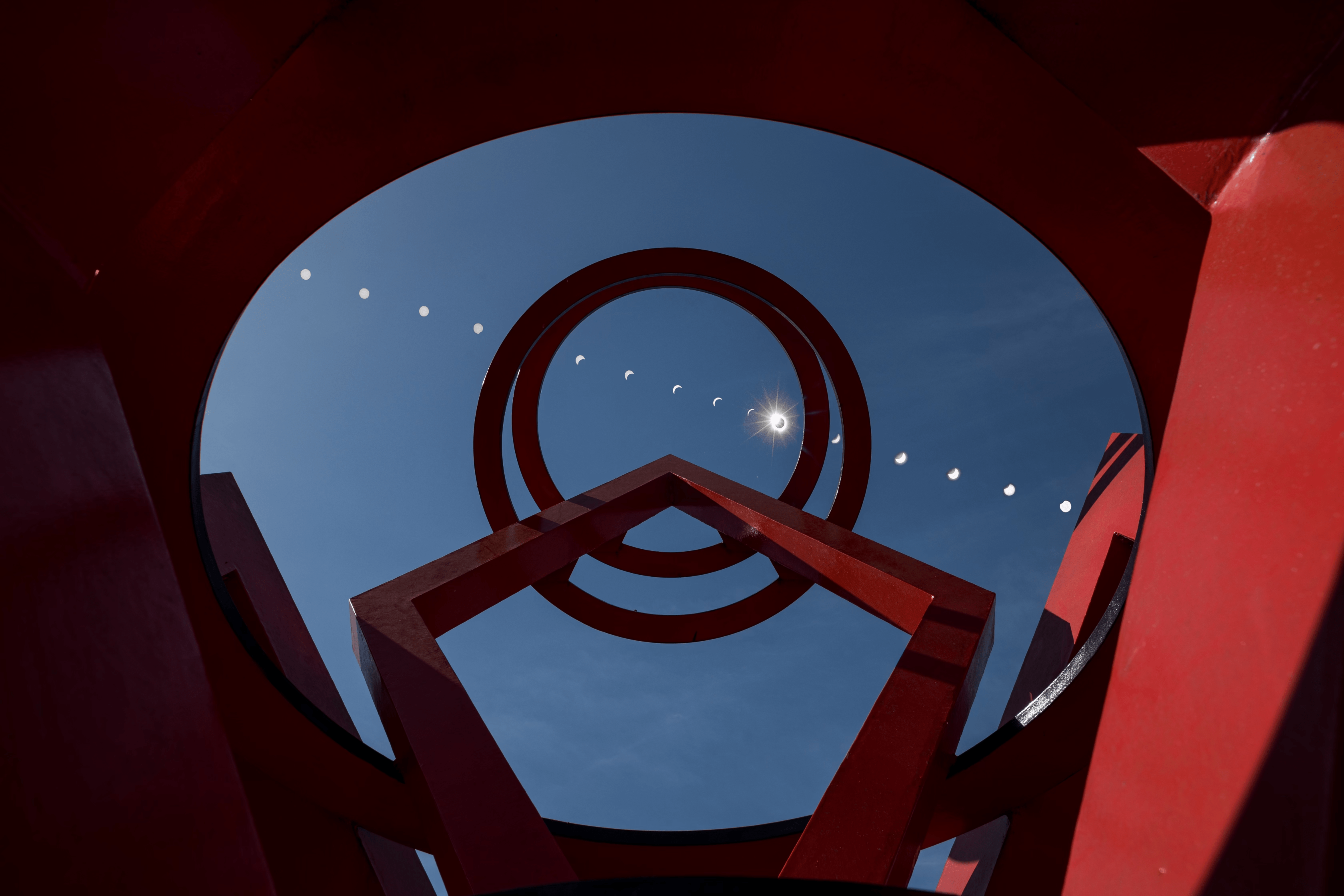
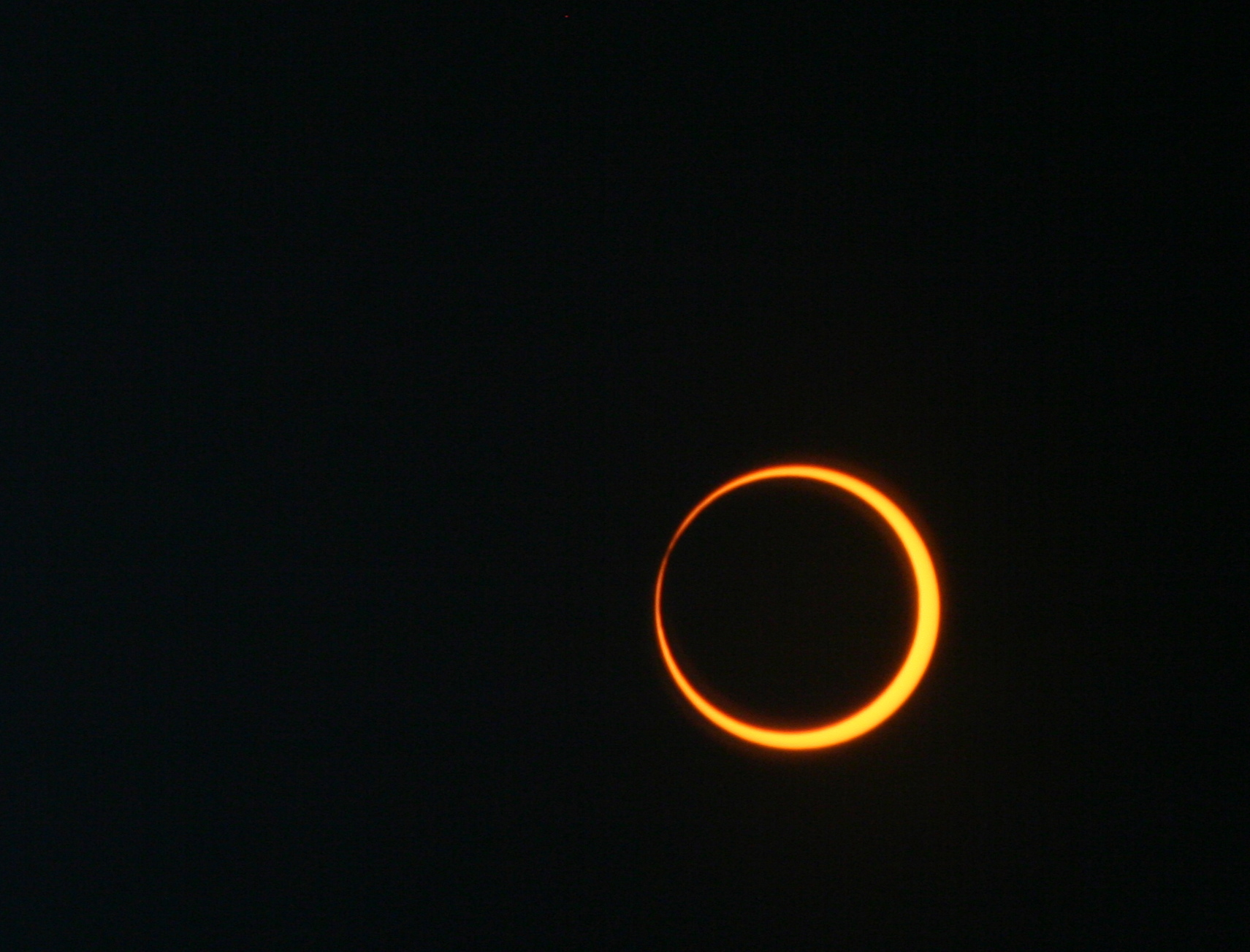
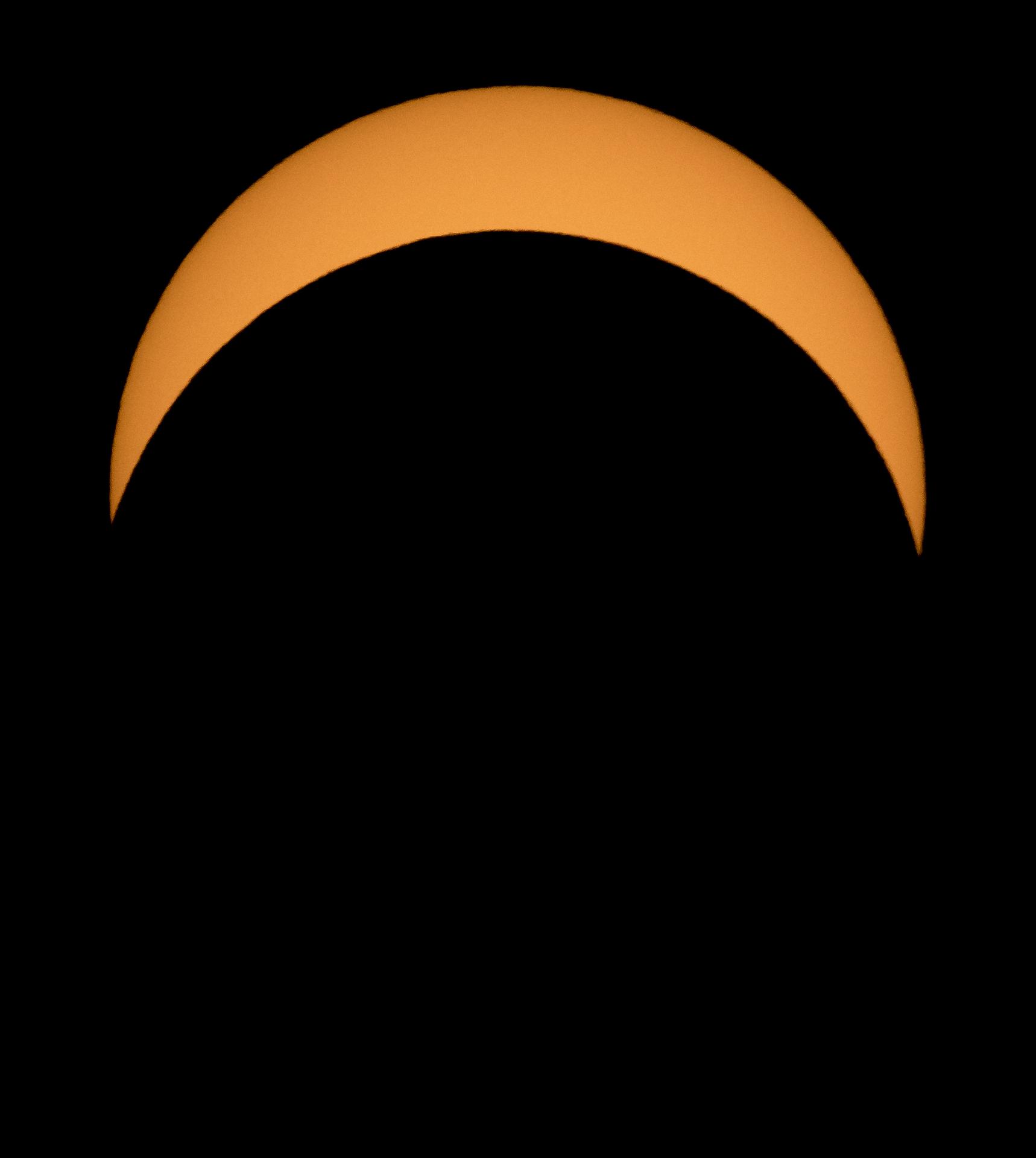
There are four types of solar eclipses: Total, partial, hybrid, and annular.
The type of eclipse that people get to see depends on how the Moon aligns with Earth and the Sun, and how far away the Moon is from Earth. There are three types of lunar eclipses: total, partial, and penumbral. At least two partial lunar eclipses happen every year, but total lunar eclipses are rare. Unlike a solar eclipse, it is always safe to look at a lunar eclipse with the naked eye.
Learn More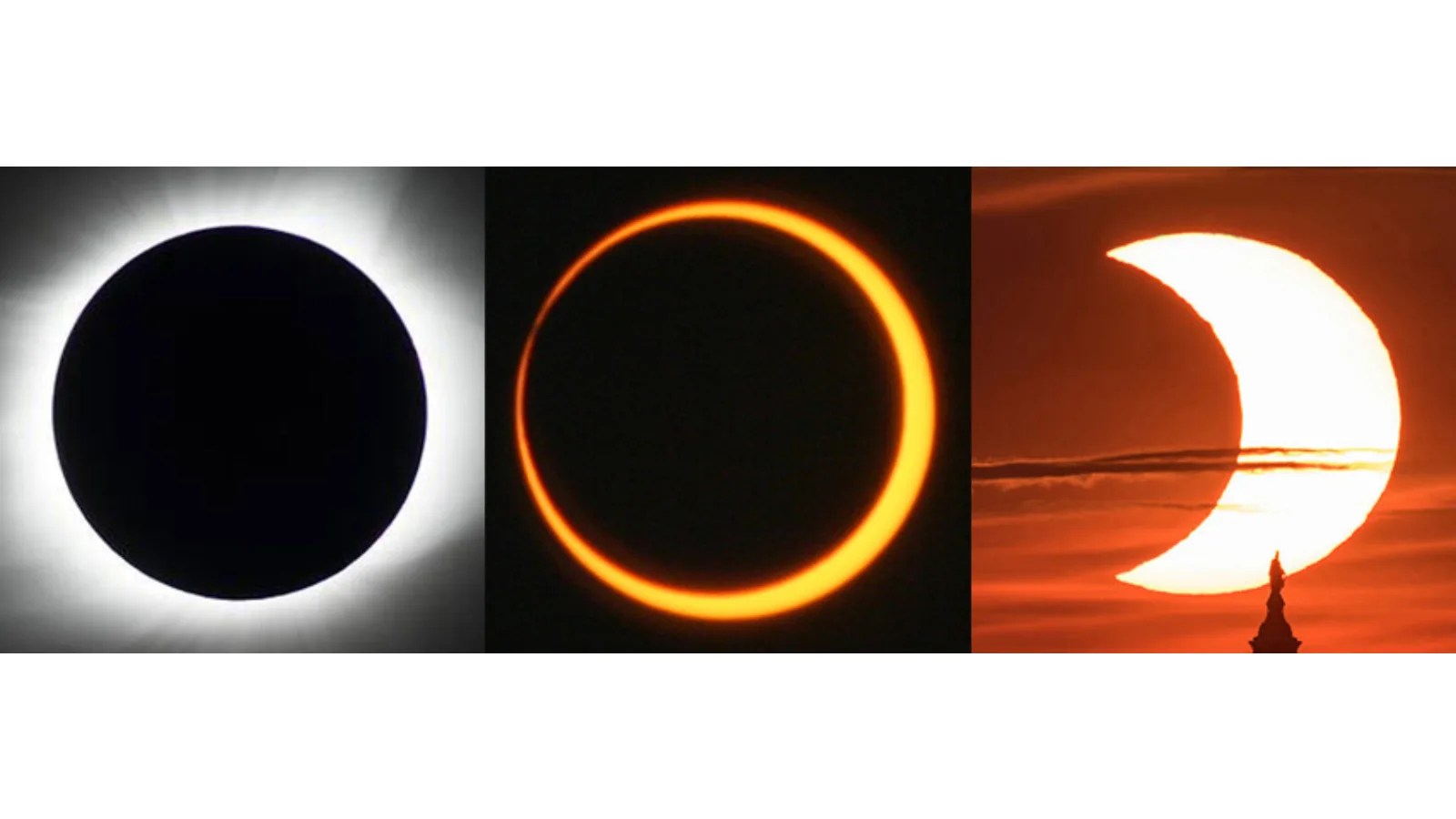
Science of Eclipses
Eclipses aren’t just beautiful – they’re great for science.
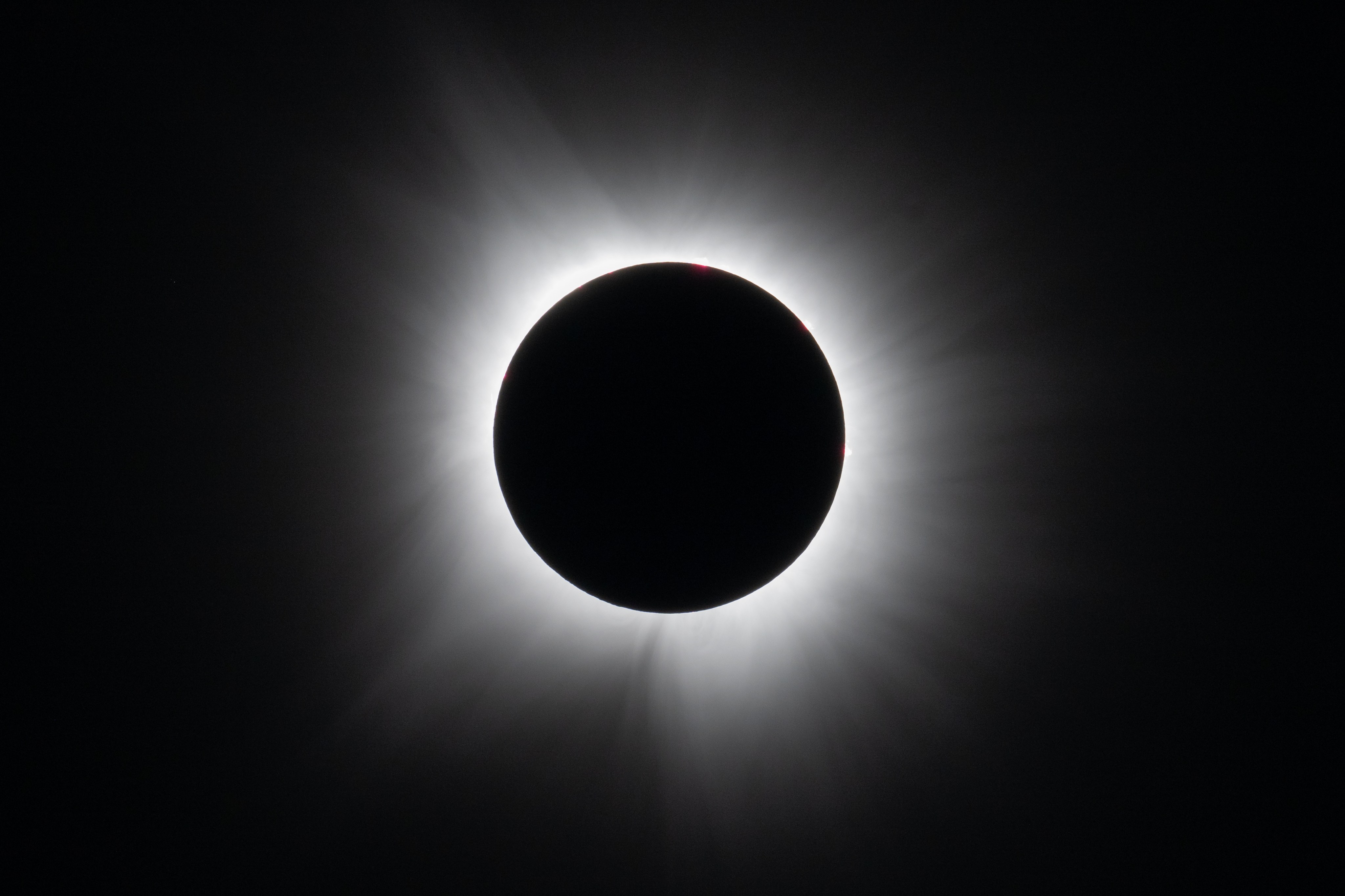
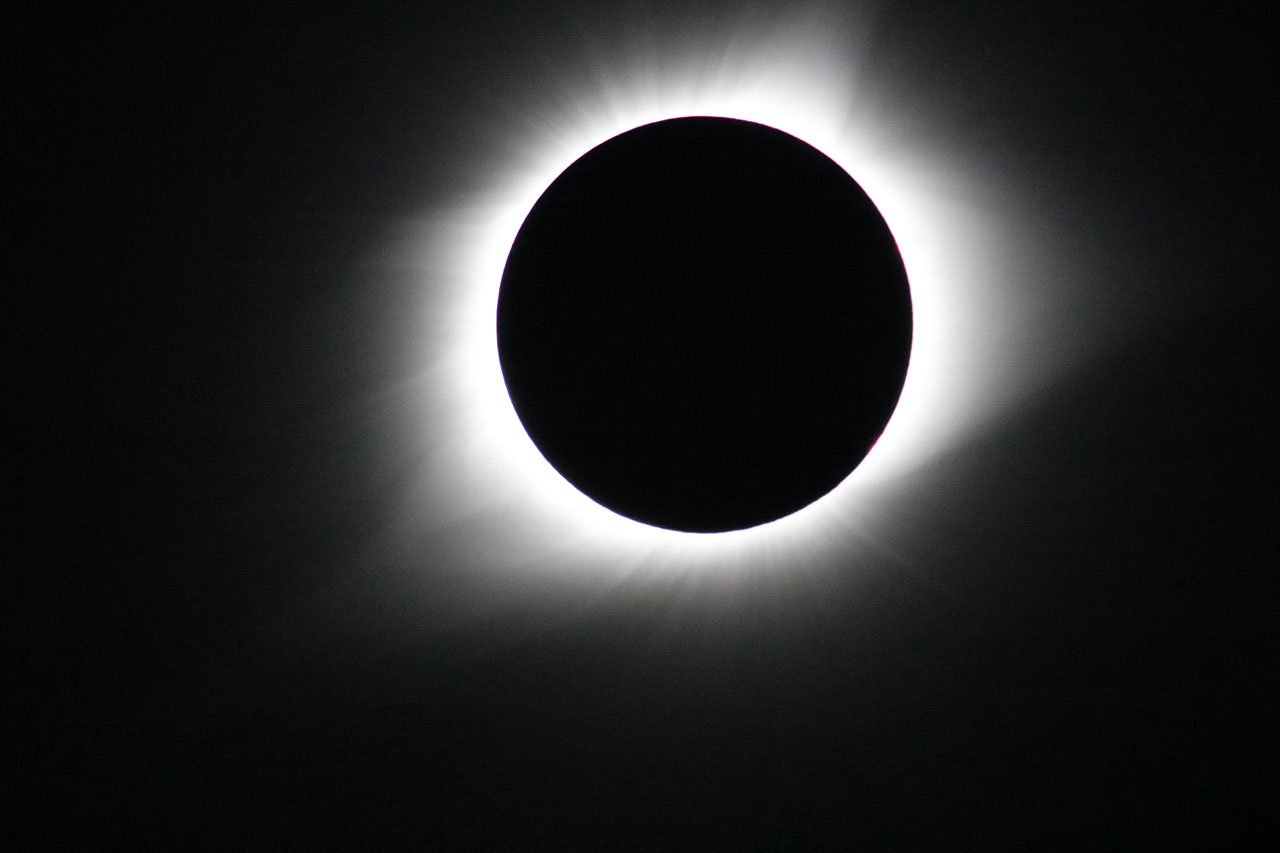
In addition to inspiring artists and musicians, eclipses have driven numerous scientific discoveries. For over a century, solar eclipses helped scientists decipher the Sun’s structure and explosive events, find evidence for the theory of general relativity, discover a new element, and much more. NASA scientists still study eclipses to make new discoveries about the Sun, Earth, and our space environment. Total solar eclipses are particularly important because they allow scientists to see a part of the Sun’s atmosphere – known as the corona – which is too faint to see except when the bright light of the Sun’s surface is blocked.
Learn More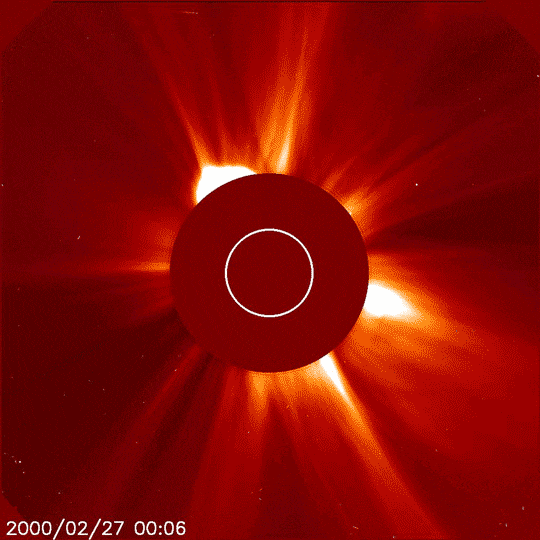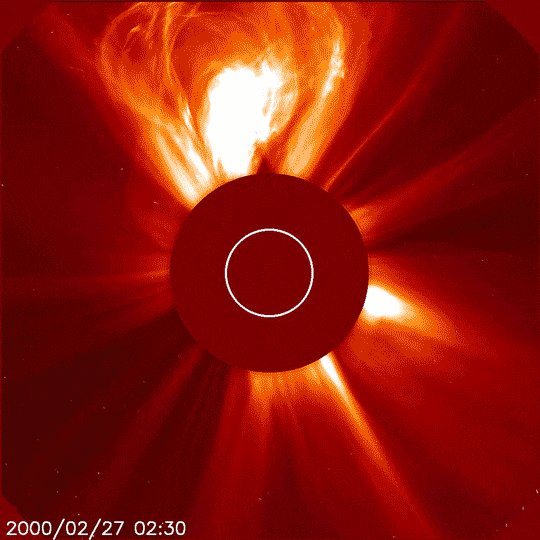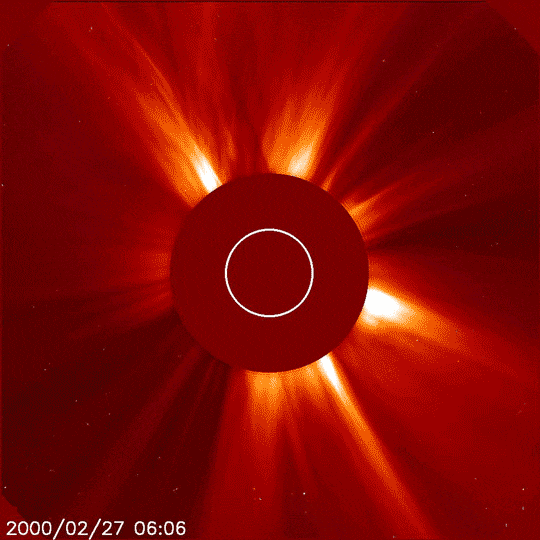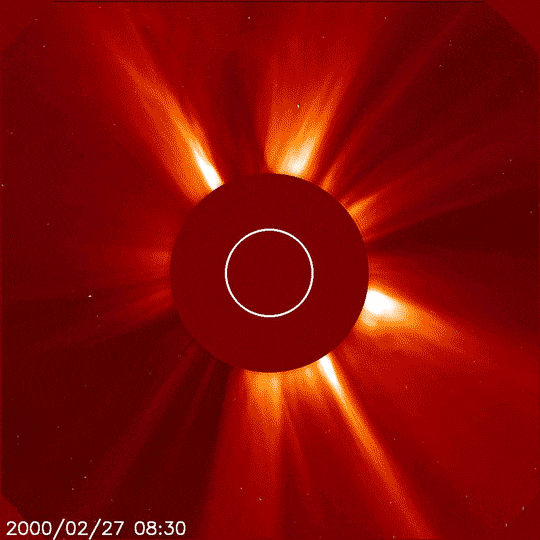
History of the Eclipse
Eclipses have fascinated humans from the beginning.
Throughout time, humans have had different interpretations of and reactions to these striking celestial events. In fact, historical records of eclipses from scribes in Anyang, China, helped astronomers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory to determine how Earth’s rotation has changed over time. Determining exactly when the eclipse was seen and where the Moon's shadow fell on Earth helped the scientists calculate the rate of Earth's spin. The eclipses they used for this research were in 1226 B.C.E., 1198 B.C.E., 1172 B.C.E., 1163 B.C.E., and 1161 B.C.E.
Learn More